Home screen
The Input Preprocessor is used to build and manage input distributions for all types of projects supported by Uptimai software. You can choose the type of input distribution best fitting to your project, set boundary conditions for them, and also visualize and check resulting distribution shapes. It is highly recommended to examine all inputs and their compatibility with the Uptimai software, especially when these are prepared in an external application or script. It prevents possible computation fails or misinterpretation of results.
How to use the interface
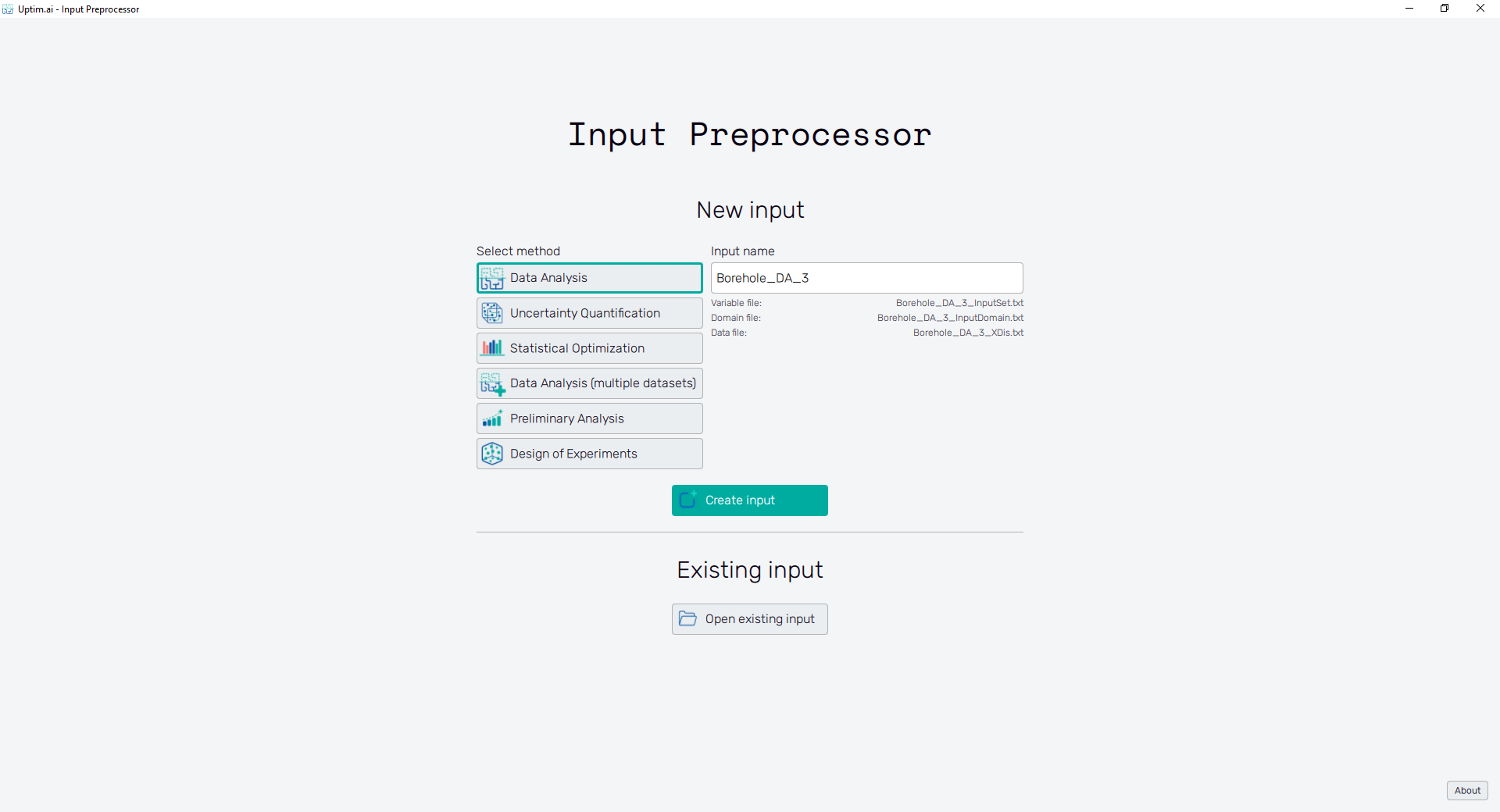
In Figure 1, it can be seen the initial state of the application's window which is split into two main sections. Here the user can either create a new set of input files or work with already existing ones.
The About button on the bottom right shows the menu dedicated to accessing the link to this document (Help), contacting Uptimai company to get the support (Company), and showing the information about the currently installed version of the program (Version).
New input
Under the New input section of the software, you can start to prepare input files needed for the work with other programs from the Uptimai family. First, the method intended to be used further has to be chosen from options found under the Select method. Currently, it is possible to prepare inputs for six methods of the Uptimai Solver and DoE scheme:
- Data Analysis : Building the mathematical model from already existing data, e.g. results of performed experiments. The postprocessing of the model offers the same features as in the case the Uncertainty Quantification method.
- Data Analysis (multiple datasets) : Generating multiple mathematical models from already existing data at the same time. Mainly it is running several instances of the Data Analysis method, with the addition of a comparison of the models at the end.
- Uncertainty Quantification : Building the mathematical model describing how changes in input variables propagate and affect the observed outputs. The data is obtained from the third-party computational software coupled with the Uptimai Solver. The model can be analysed in the Postprocessor tool to obtain a visual description of the results.
- Statistical Optimization : Finding the optimum zone of the domain, taking into account the uncertainties of the variables. It builds several models at different scales of the problem.
- Direct Optimization : Searching for the global optimum of the output. It uses enhanced strategies for more efficient optimization process with faster convergence.
- Preliminary Analysis : Analysis showing the sensitivity of the variance of results to input variables. A simplified process that does not require building the full surrogate model, significantly reducing the number of samples is required.
- Design of Experiments : Preparing design space sampling according to classic DoE methods such as Latin Hypercube Sampling. Also, suitable for complementing of an existing DoE scheme with new samples.
The Create input button brings the user to the Input preparation screen which corresponds to the selected method. The software suggests a generic name for the set of input files in the Input name field. For each input, there is a set of files defining the domain of the project and the sampling:
- Variable file
:
<prefix>_InputSet.txtdescribes the definition of probability distribution types and their parameters for each input variable - Domain file
:
<prefix>_InputDomain.txtcontains the settings of the probability distribution boundaries and the position of the nominal sample - Convergence file
:
<prefix>_Convergence.txtcontains the reduction threshold for each input. Only created in Statistical Optimization problems. - Data file
:
<prefix>_XDis.txtholds the Monte Carlo sampling of the domain used for the model propagation and visualizations. - DoE file
:
<prefix>_Design.txtdescribes settings of the Design of Experiment sampling. - Constraint file
:
<prefix>_Constraints.jsondescribes the definition of constraints for the Direct Optimization method.
The software generates automatically names of files related to the particular set of inputs.
Nevertheless, the name prefix can be modified by the user. These files are
saved into the inputs folder inside the current project. Also, the information about the
created input and its corresponding files is written into the <project>.uptim file of the
current project. This file with meta information should not be edited by users.
In particular cases, (especially when solving Data Analysis problems, processing a whole batch of cases, etc.) it is helpful and time-saving to prepare required input files in an automated way. For this purpose, custom Plugins can be created and used.
Existing input
When there are any already existing sets of input files, these can be accessed via the
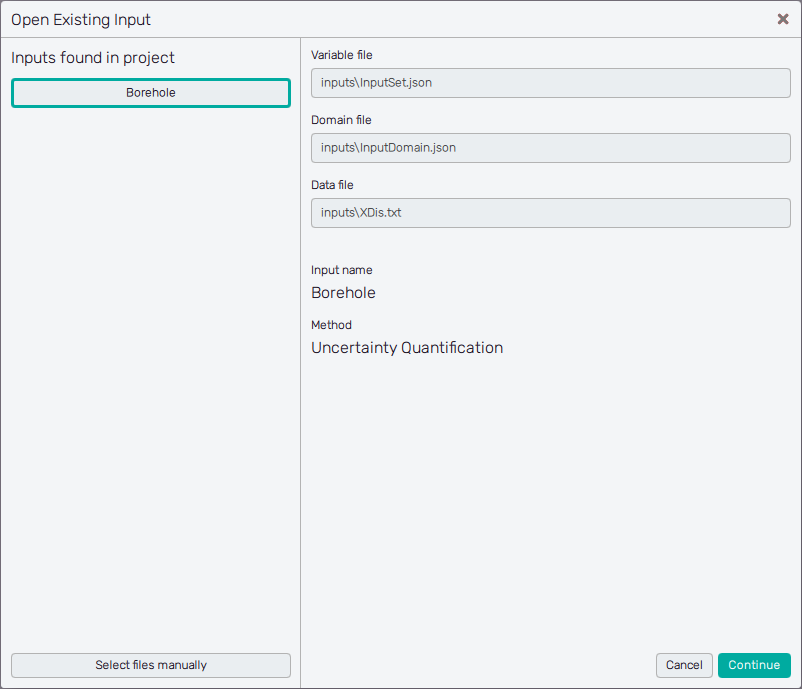
Open existing input button. This will open the Open Existing Input dialog, as shown
in Figure 2. In case there are inputs recognized for the current
project (need to be listed in the <project>.uptim file and found in their destinations),
you can select them by clicking from the list appearing on the left under the Inputs
found in project sign.
For each selected input the list of corresponding files will be displayed on the right together with the input name and the method of the Uptimai Solver. Then, the Continue button will bring the user to the input preparation screen which corresponds to the selected method. The Cancel button closes the dialogue and shows the initial screen of the Input Preprocessor.
If no input was found in the project, either because it was not listed in the
<project>.uptim file or the user wants to use input from another project,
it is possible to select input files manually using the Select files manually button.
After selecting the Variable file containing the definition of input variables'
distributions and the selected Method, the program will allow the user to select the other
relevant files for your type of problem. The Input name
can be edited, meaning it is possible to share the same files for multiple sets of inputs -
e.g. Variable file, Domain file, and Data file of the
Uncertainty Quantification
method can be used for the Data Analyzer method, which has then two additional files
describing existing data samples together with their results that are used for training of the
model.