Home screen
The Uptimai Result Postprocessor is a tool where users can perform a comprehensive analysis of results obtained in methods of Uptimai Core Solver. The tool is intended for work with result files of the Uptimai process. The complete guide to supported filetypes can be found in a separate section of this document. The software also allows the user to export plots and tables with particular findings shown in each feature of the program.
Supported file types
The primary purpose of the Uptimai Postprocessor is to open and read files generated using the Uptimai Core Solver. These contain the surrogate mathematical model and the data necessary for its analysis. These are:
-
.upst : Store file containing the mathematical model. It is generated at the end of the Uptimai Core Solver computation. It provides the data required for the evaluation and plotting of the results. These may vary according to the method of the solver.
-
.upsg : Store file related to the Statistical Optimization and the Data Analysis (multiple datasets) method.
-
.itr : Iterative store file containing the database of computed samples called in the process of learning the mathematical model. This database can be used to restore, check, and repair the model-learning run.
| File | .itr | .upsg | .upst |
|---|---|---|---|
| Preliminary Analysis | |||
| Uncertainty Quantification | |||
| Data Analysis | |||
| Data Analysis (multiple outputs) | |||
| Statistical Optimization | |||
| Direct Optimization |
Besides, the Postprocessor can read some of the generally used types of files, such as pictures, plain text files and comma-separated tables, Python and shell scripts, JSONs and some others. A list of supported formats can be found below:
- .txt
- .csv
- .jpg/.jpeg
- .png
- .py
- .json
- .sh/.bat
- .stl/.obj/.step
How to use the interface
In Figure 1, the initial state of the application's window in two variants. The screen is split into two sections. On the left side of the window there is the Project files frame showing either the selected important files in the project or the whole file structure of the current project folder, depending on the position of the switch on the top side of the sidebar. The frame itself is collapsible by the mouse clicking on its label or the < symbol. The user can open and close subfolders shown in the directory tree by double-clicking.
Files can be listed in two ways:
- Overview : Groups files of the project according to their type, so it is easy to access e.g. all Result files including those stored in subfolders. This mode also supports the search feature having its enry field above the list of files.
- Project folder : Shows the complete directory-tree structure of the project folder. All subfolders can be entered and closed with mouse double-clicking.
Double-clicking also opens files to be shown in the Postprocessor, here is the list of currently available supported file types. Opened file appears in the right section of the window as a new tab. Another way to open a file is through the right-click menu, accessing the following features:
- Open : Opens the file in the same way as in the case of double-clicking it in the project directory tree.
- Open in New Tab : Always opens the file in a new tab. Unlike the standard Open method, this one allows to show multiple tabs with the same file. This is helpful when multiple postprocessing features of the same file need to be seen next to each other.
- Open in Right Split : Directly splits the workspace and arranges the new tab to the right from an existing one.
- Open in Default App : Opens the file in the system default application for the type. Useful for file types not featured in supported file types, especially for non-Uptimai files.
- Compare Outputs : Starts the dialogue of the dedicated feature where the user can directly compare the results of two outputs of the project and their statistical properties.
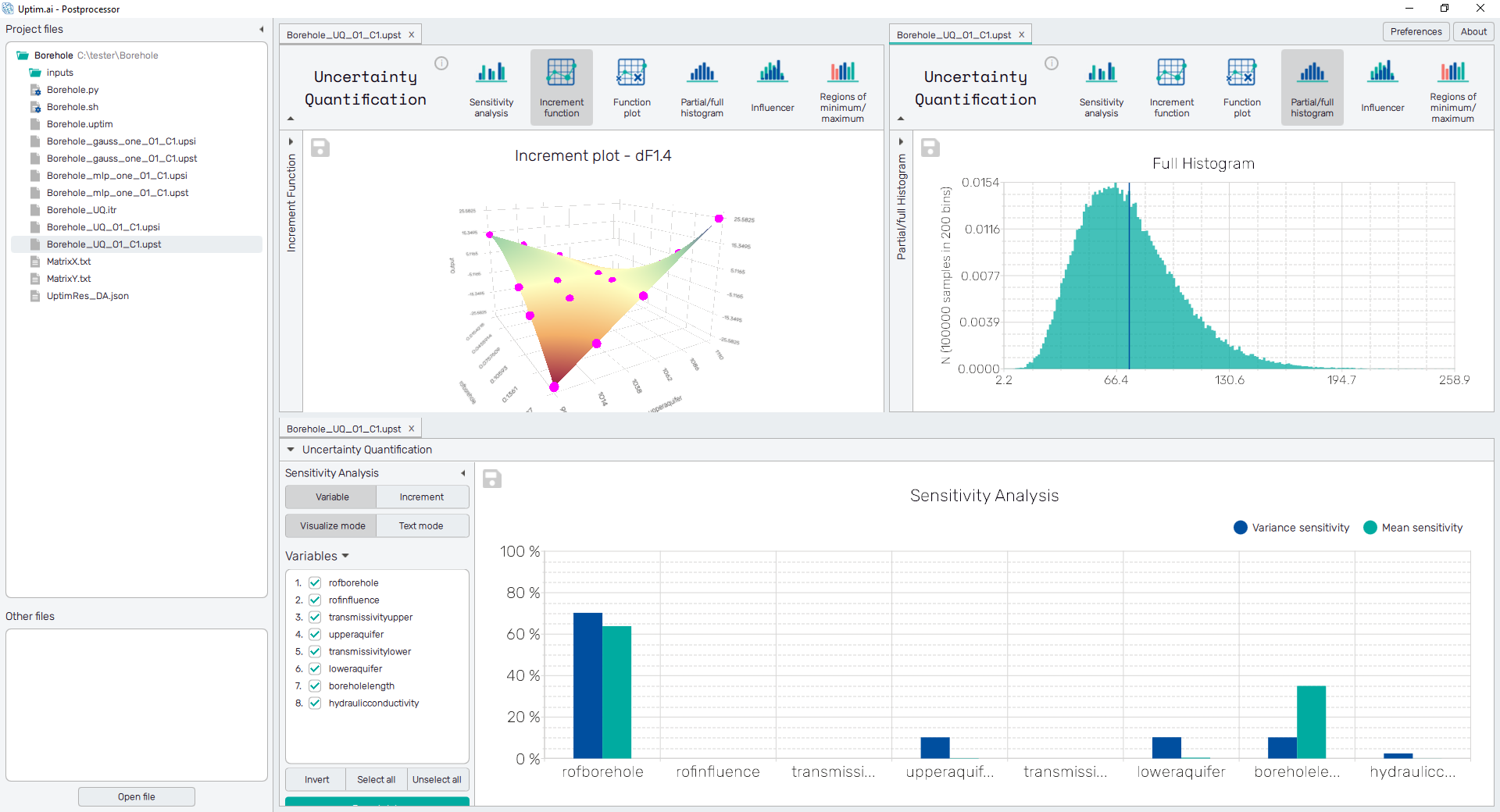
The general appearance of the tab is shown in Figure 2. Each tab has its label on the top together with the X symbol closing the tab. When multiple tabs are open, they can be rearranged with mouse-dragging of their labels to observe more than one file at a time. If one of the Uptimai result files is opened, a bar with postprocessing features is shown on the top of the tap. The bar also shows on the left if the opened file was identified as an Iterative file or refers to the method used to build the model in the result file. Right next to it is the ⓘ icon accessing all Case file details with the info about the used hardware, OS, version of the Uptimai software, the setup, and the date. In case there are any warnings produced by the Core Solver, the icon is shown in orange color and in the Case file details, the user can access those warnings.
The right top of the screen holds two additional buttons. The Preferences button opens the dialogue with the setting of the general behaviour of the Postprocessor. Users can enable the Multiprocessing to speed up features of the program, mainly the process of model interpolations. The About button shows the menu dedicated to accessing the link to this document (Help), contacting Uptimai company to get the support (Company), and showing the information about the currently installed version of the program (Version).
List of Postprocessor features
The Postprocessor offers a variety of features for data analysis and plotting. These are accessed through icons shown in the bar at the top of the tab with the opened file. The list of features currently available for the opened file may vary based on the method used by the Uptimai Core Solver, and according to the filetype which is currently opened. All features included in the program are:
- Sensitivity analysis : Sensitivity analysis tries to establish the influence of the input variable on the output of a mathematical model or system (numerical or otherwise). Based on the results of the sensitivity analysis, inputs relevant to the problem can be focused on.
- Increment function : Increment function plot visualizes the influence of a selected increment function. Each increment function represents a separate increment to the final model caused by uncertainties in the selected dimension (or combination of dimensions) of the domain.
- Function plot : Function plot is used to visualize the behaviour of the function of interest. Shows absolute output values through the design space, either as a value for a specified combination of inputs or as a function of up to three selected input variables.
- Partial/full histogram : A histogram is a representation of the distribution of numerical data. It is an estimate of the probability distribution for an uncertain output/s. This allows visualizing how each part of the variable influences the final distribution.
- Influencer : Influencer compares the final distribution against a distribution with selected increment functions or input variables neglected from the final model. This allows a comparative visualization of the influence of the aspects on the statistics of the problem.
- Regions of minimum/maximum : Regions of minimum and maximum represent a statistical approach to optimization. Distribution shapes of input variables proposed here follow general trends in the mathematical model and result in probability distribution shapes with either decreased or increased mean value.
- Parallel Coordinates plot : The Parallel Coordinates plot is a visualization for exploring high-dimensional datasets. Each input or output variable is represented by its own vertical axis, and each design point (sample) is drawn as a polyline intersecting all axes at its respective values. In addition, each axis distribution is visualized using a histogram.
- Postprocess : Postprocessor shows the convergence history of the mathematical model learning process. Also, it contains the data about precision approximations.
- Postprocess (Data Analysis) : Shows the precision of the computed model, by comparing the real values against the model output values. There are multiple views, including the direct comparison of output values and the display of model errors.
- Model info : List of models used to build the final result together with their detailed setup and history of iterations.
- Optimized histograms : Optimized histograms are the result of the Statistical Optimization method, proposing new domain ranges to achieve prescribed optimization criteria. Users can see probability distributions of input variables used in each iteration of the optimization process and related distribution functions of interpolated function values.
- Pearson correlations : Table of Pearson correlation coefficients of all models generated on the same domain.
- Pearson correlations (anomalies) : Table with likelihood of the anomaly occurrence being present on the same position for each combination of models generated on the same domain.
- Anomalies position : Positions of detected anomalies and their distribution on the range of the selected input value. Direct identification of correlated anomalies on multiple models generated on the same domain.
- Result visualization : Shows the output of the Direct optimization method. This page shows the final population of the optimization process.
- Input visualization : Shows the output of the Direct optimization method. This page shows the final population of the optimization process, plotted against the values of the input variables.
- Data summary : Shows the output of the Direct optimization method. This page summarizes the optimal value found by the optimization and it's properties, as well as the optimization method used.
- Convergence properties : Shows the output of the Direct optimization method. This page summarizes the convergence of the optimization process in relationship with the input variables.
- Iterations overview : Shows the output of the Direct optimization method. This page shows how the optimal known sample evolved throughout the optimization process.
- Compare outputs
: Direct comparison of two different outputs of the same project. This feature opens
a new tab since another set of postprocessing features is available for
comparison. The user needs to be sure that the compared
.upstfiles are based on the same set of inputs. - Data propagator
: Direct comparison output values loaded from a file against their approximations based on the
model. The user needs to be sure that the compared dataset is compatible with the current
.upstfile. - PDF report
: Summary of visual and data outputs of available features of the postprocessing exported
as an automatically generated
*.pdfdocument.
| Postprocessor Feature | Preliminary Analysis | Uncertainty Quantification | Data Analysis | Data Analysis (multiple outputs) | Statistical Optimization | Direct Optimization |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Sensitivity Analysis | ||||||
| Increment Function | ||||||
| Function Plot | ||||||
| Partial/Full Histogram | ||||||
| Influencer | ||||||
| Regions of Minimum/Maximum | ||||||
| Parallel Coordiinates Plot | ||||||
| Postprocess | ||||||
| Model info | ||||||
| Optimized Histograms | ||||||
| Pearson correlation | ||||||
| Pearson correlation (anomalies) | ||||||
| Anomalies position | ||||||
| Result visualization | ||||||
| Input visualization | ||||||
| Data summary | ||||||
| Convergence properties | ||||||
| Iterations overview | ||||||
| Compare Outputs | ||||||
| Data Propagator | ||||||
| PDF Report |