Uncertainty Quantification
This is a basic tutorial of Uptimai software prepared to give a first introduction to the suite,
and how to run the different features. To complete this tutorial will be needed Uptimai
software and a *.zip file with some complementary files needed for the example problem to be
solved. The Borehole.zip file can be found inside Member area ->
Download -> Tutorial cases.
The *.zip file contains the whole project folder, so the user can start at any step of the given
tutorial. Nevertheless, if the user wants to fulfil the tutorial from the beginning, only the
Python script Borehole.py will be necessary, as all the other files will be generated during
the process.
This tutorial will show you:
- How to run each program of the package
- What are the main features of each program and how to use them
- What are the results you can expect
- How to export and store output data
- How to deal with basic issues you can encounter during the process
Part 1: Main Interface
1.1: Starting the program
Open Uptimai software, starting the Launcher GUI. You can use the shortcuts if this option was selected during the installation process, or find the executable inside the installation folder.

1.2: Creating the project
Create a New Project with the button of the interface. You will have to choose an empty folder where all the project files will be located. The name of the folder will become the name of the project, in this example, we will use the name Borehole. You can create the folder directly from the interface.
Once you have created the project a *.uptim file will appear inside your project folder.
That file is used as a flag so the folder is recognized as an Uptimai project and contains
information about its available inputs and setups.
1.3: Start working on the project
Now, you have access to all the different features that conform to the Uptimai suite. In this tutorial, we will use them one by one.
Part 2: Input Preprocessor
2.1: Running the Input Preprocessor
The first step of all projects is always the Input Preprocessor, which can be opened directly from the main interface. The initial state can be seen in Figure 3.
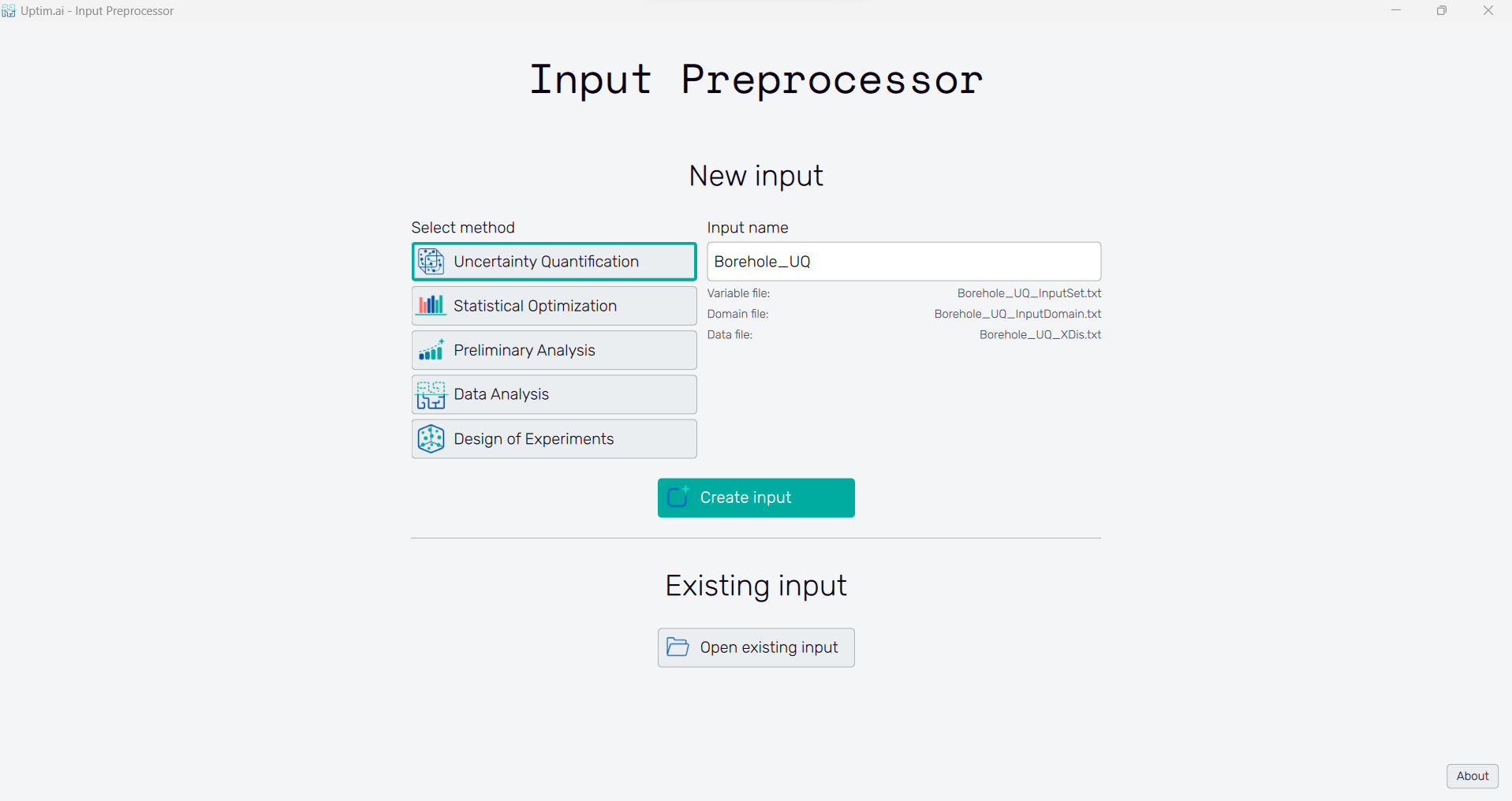
2.2: Inputs for the Uncertainty Quantification method
In this tutorial, we will select the Uncertainty Quantification method. It is possible to modify the Input name, but for simplicity, we will maintain the default name suggested by the software. Then, we can click the Create input button to start generating all the input files. You can see their names below the Input name entry.
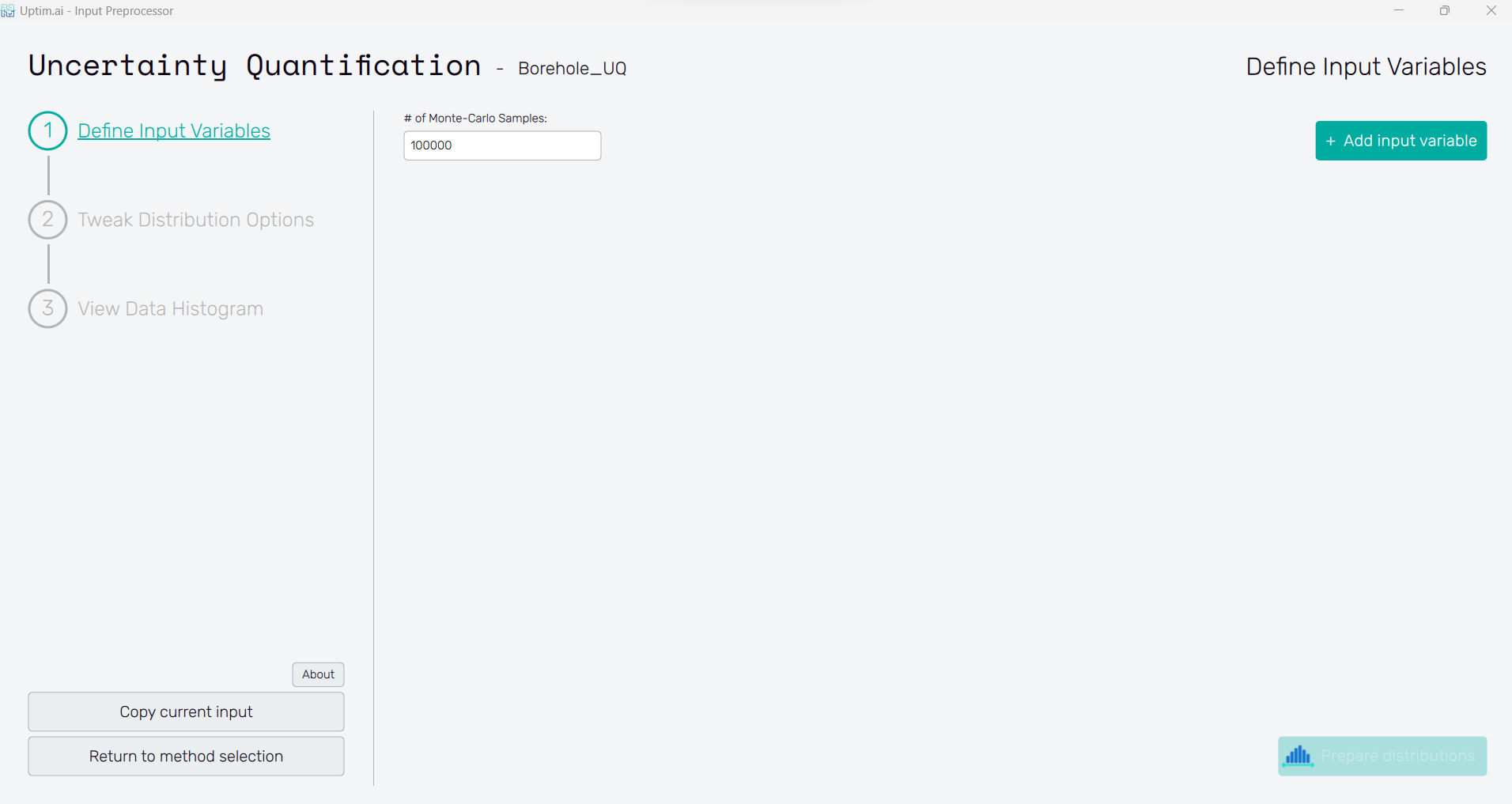
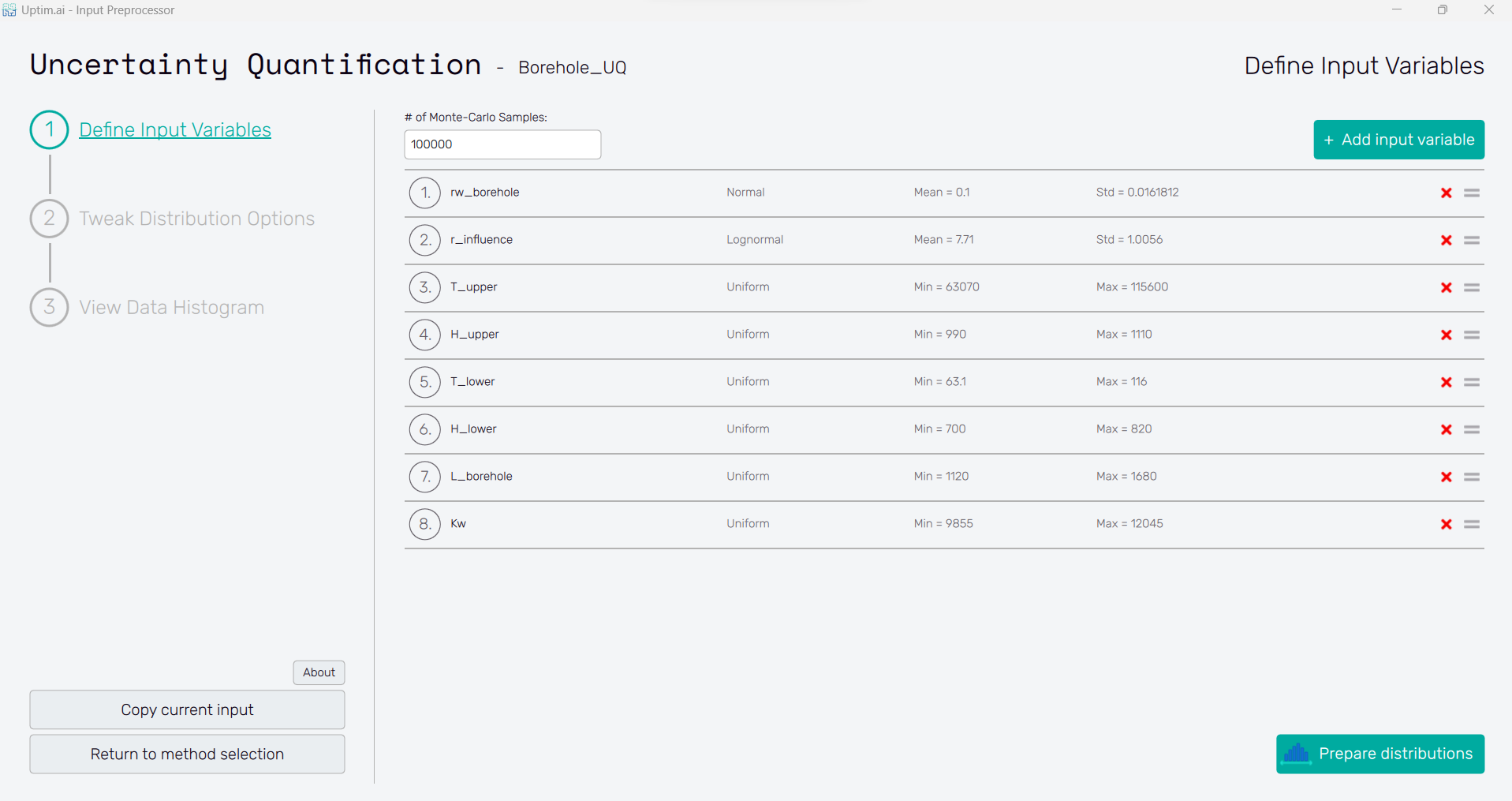
2.3: Add input variables
In this case, we have 8 input variables, so we will use the Add input variable button at the upper right to generate 8 variable spots.
2.4: Define input variables
Insert the following distribution to each variable. Remember to press the Confirm button to save the changes after editing each variable. In the end, you should have the same settings as in Figure 5
Open to view Input Distributions
| Name | Type | Parameter 1 | Parameter 2 |
|---|---|---|---|
| rw_borehole | Normal | 0.1 | 0.0161812 |
| r_influence | Lognormal | 7.71 | 1.0056 |
| T_upper | Uniform | 63070 | 115600 |
| H_upper | Uniform | 990 | 1110 |
| T_lower | Uniform | 63.1 | 116 |
| H_lower | Uniform | 700 | 820 |
| L_borehole | Uniform | 1120 | 1680 |
| Kw | Uniform | 9855 | 12045 |
2.5: Preparing distributions
Click the Prepare distributions button and continue with the Tweak distribution options to move forward.
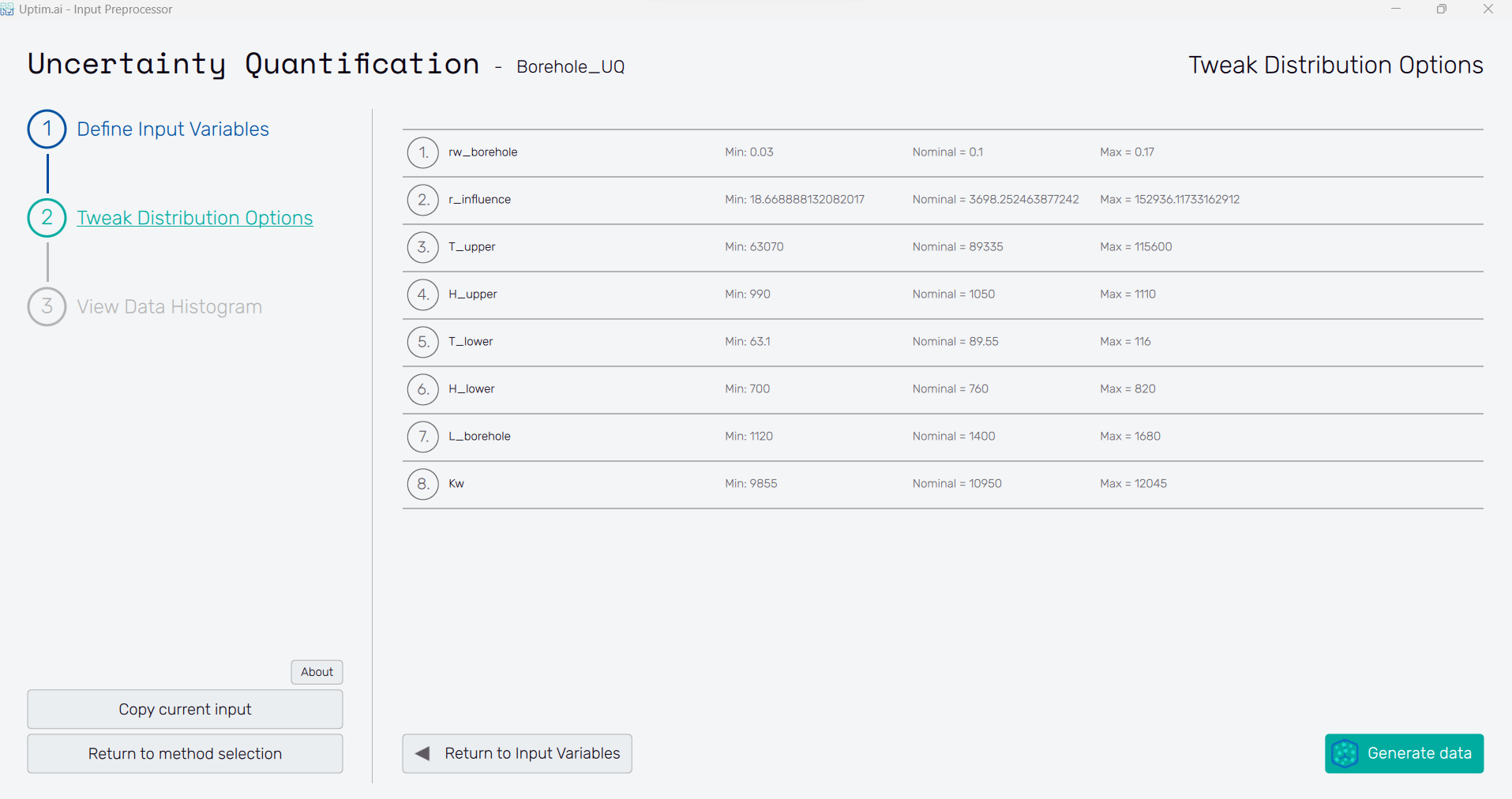
2.6: Tweek distribution options�
At this point, we can tune the domain of each variable. In this case, as variable number has a normal distribution, we will crop the tails to ensure we don’t have any samples outside the domain. Set the minimum value to 0.03 and the maximum to 0.17.
2.7: Generate data
Finally, we can press the Generate data button, and move to visualizing the input distributions we just created. At this point, we have generated three files that store all the information provided inside an input folder in the project folder.
Borehole_UQ_InputSet.txt: Stores the information related to the probabilistic distributionsBorehole_UQ_InputDomain.txt: Stores the information related to the boundaries of the problemBorehole_UQ_XDis.txt: Stores a Monte-Carlo set of samples used for the propagation of uncertainties
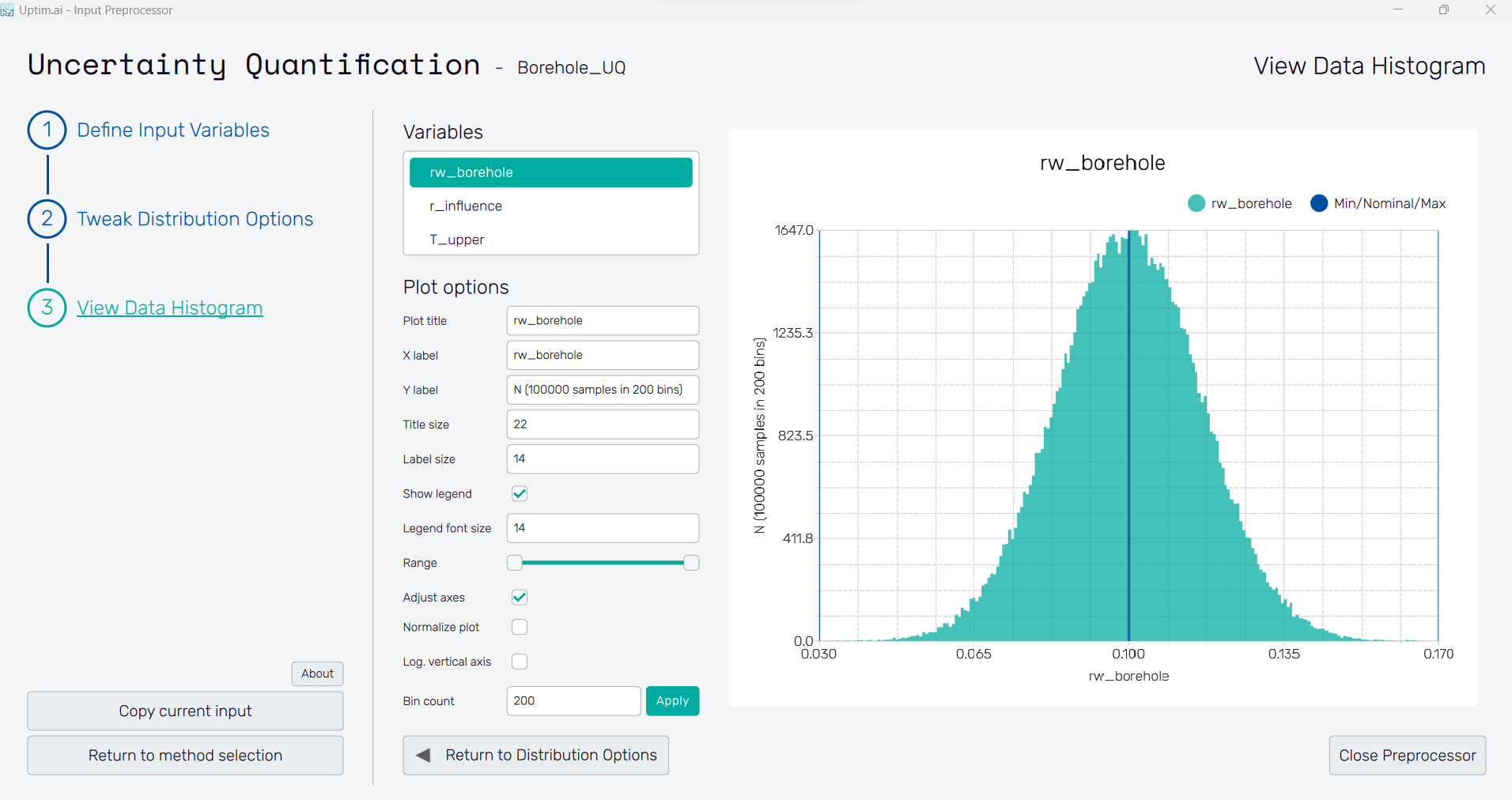
2.8: View data histogram
Visualize input distributions in the View data histogram section of the interface. Once we ensure that the histograms presented for every variable are the probability distributions wanted, we can close the Input Preprocessor with the Close Preprocessor button and move to the next tool.
Part 3: Set up Core Solver
3.1: Start the setup GUI
Once the inputs have been generated, it is time to prepare all the settings for the solver. We can do that using the Core Solver Setup, which once opened from the Uptimai main interface has the appearance as shown in Figure 8.
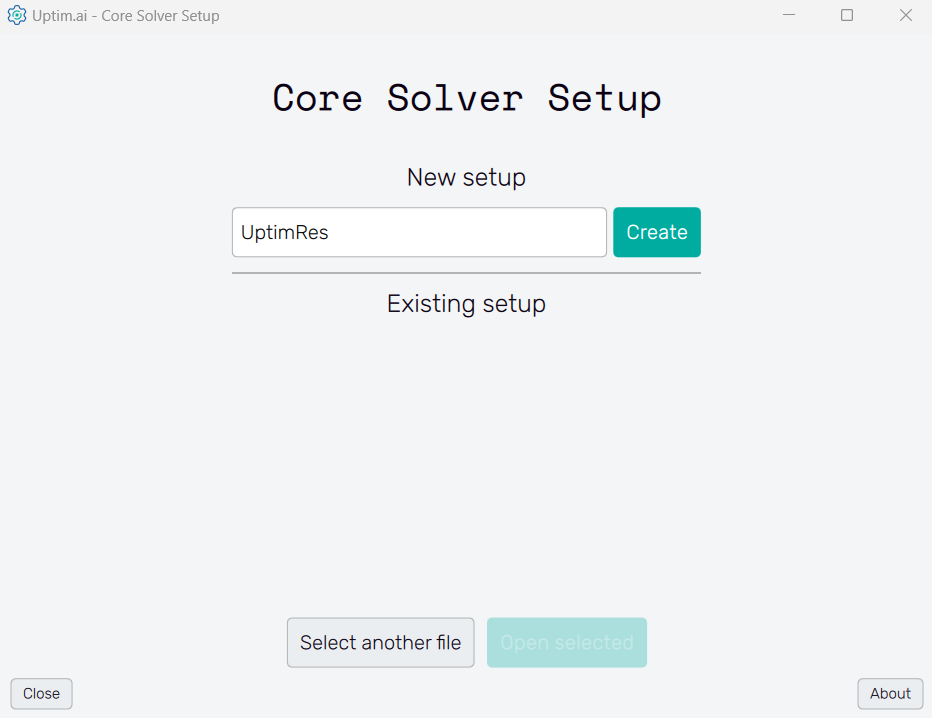
3.2: Create new setup
Once the program is opened, the first thing we need to do is to create a new setup file. We can maintain the name of the file to the default value of UptimRes, and just click on the Create button.
3.3: Select the set of inputs
Then, we will see that the Core Solver Setup has three main tabs. The first one is to select the input files that will be used in this run. As in this case, we only have one set of available inputs, we will just select that one.
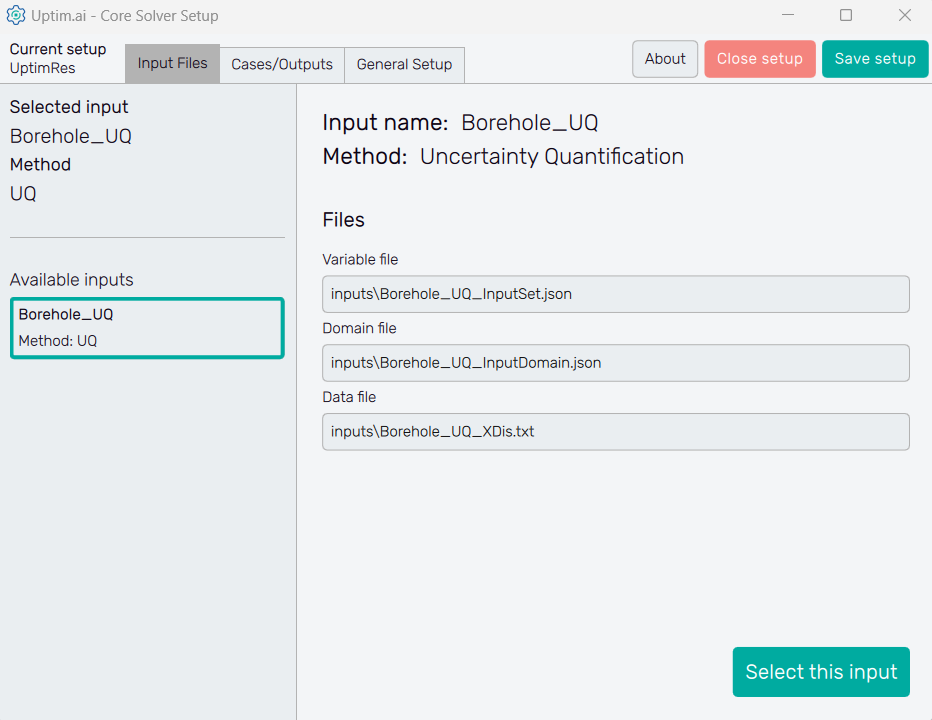
3.4: Set up the case
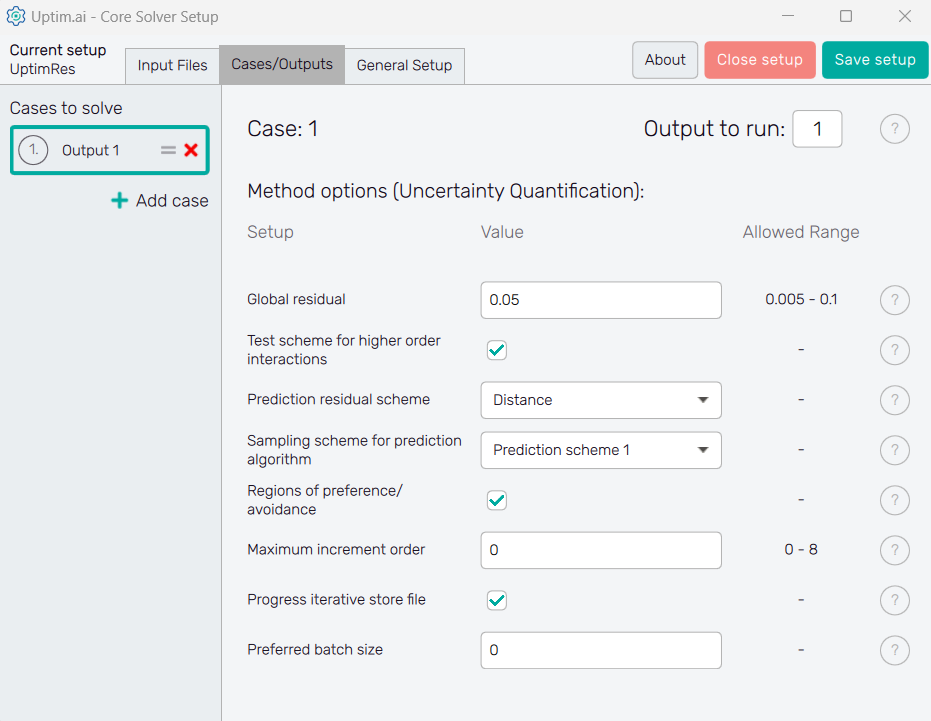
The second tab, which is Cases / Outputs, details all the settings that are used for tuning the core solver to the needs of each specific problem. Thus, there is a setup specific to the Uncertainty Quantification method we are working with. Also, there is information about which outputs we would like to study. In this case, we will leave all the parameters to the default value except the Global residual which we will reduce to 0.01, to have a very accurate model of the problem.
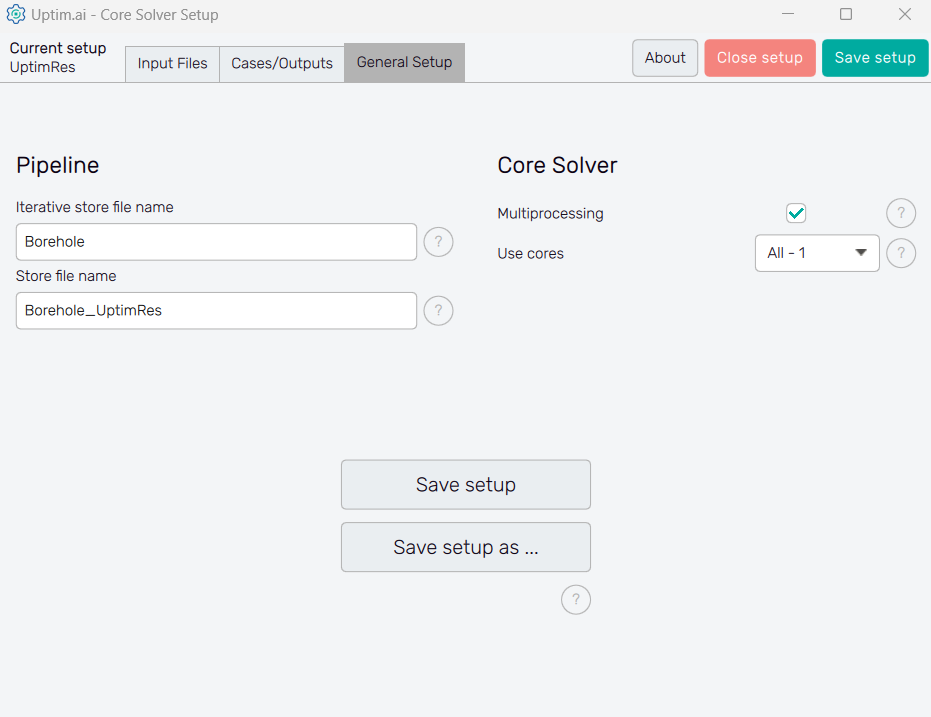
3.5: General setup
Finally, in the third tab, there is information regarding naming and other solver aspects. In
this case, we don’t need to modify anything, and we can directly save the setup. When we do that,
an UptimRes.json file will be generated in the project folder containing all the information
that we saved. That file will be used by the solver itself.
Part 4: Run Solver (Automation)
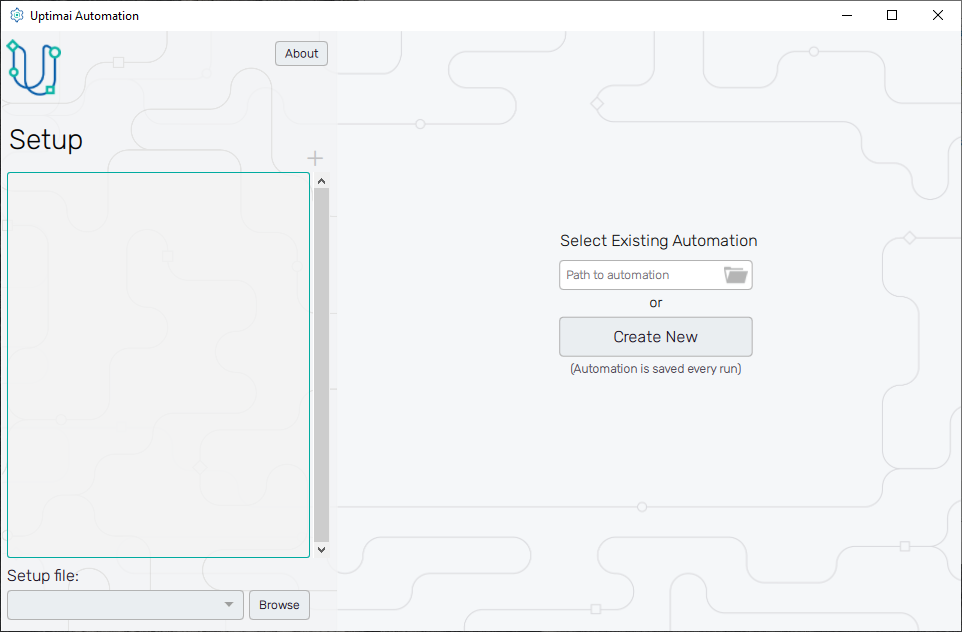
4.1: Create new automation configuration
Now, it is time to open the Run Solver (Automation) from the Uptimai main interface. We will create a new automation file using the New automation section of the screen. Here, choosing any name and clicking the Create button stores the newly created file in the project folder. In case you want to load a previously created session, select one item from the list of the Existing automation section and confirm with the Open selected button. Eventually, you can search for any automation session under the Select another file button.
4.2: Add a connection
For Uncertainty Quantification
cases, there must be third-party software that converts a set of inputs to a set of
outputs, so we can adaptively create the model. In this tutorial, this role is played by
a Python script called Borehole.py that you can download from the
Member Area as a part of the tutorial project, so the first step of this process would
be to download and paste the script into your project folder.
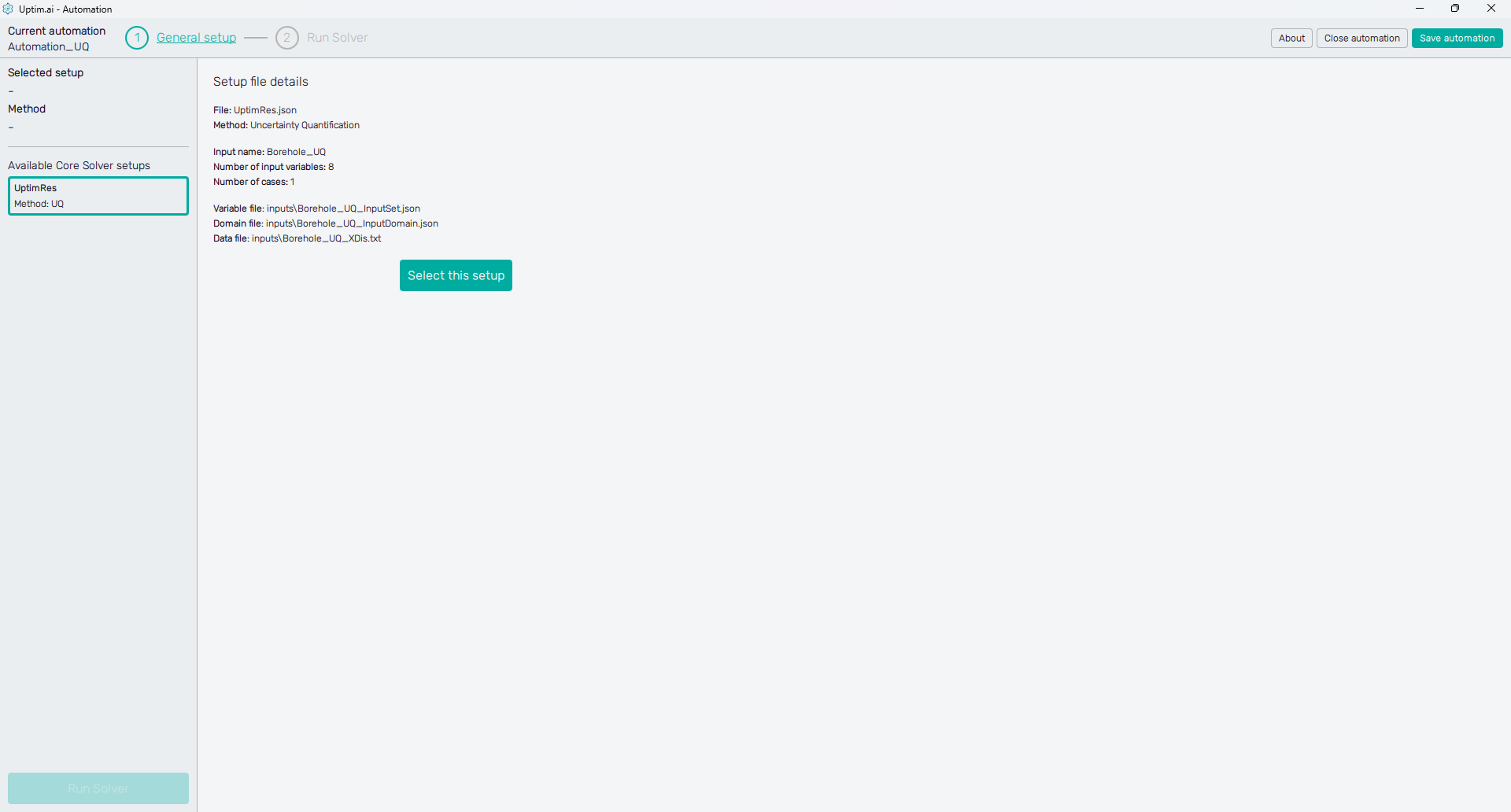
The next step is to select the setup you've created in Part 3 of the tutorial. Our setup file UptimRes should be in the list of Available Core Solver setups shown on the left panel of the screen. The method 'UQ' (Uncertainty Quantification) was identified automatically to make the navigation through list items easier. Once the setup item is clicked, you can see the Setup file details. Then, confirm the selection with the Select this setup button.
4.3: Core Solver settings
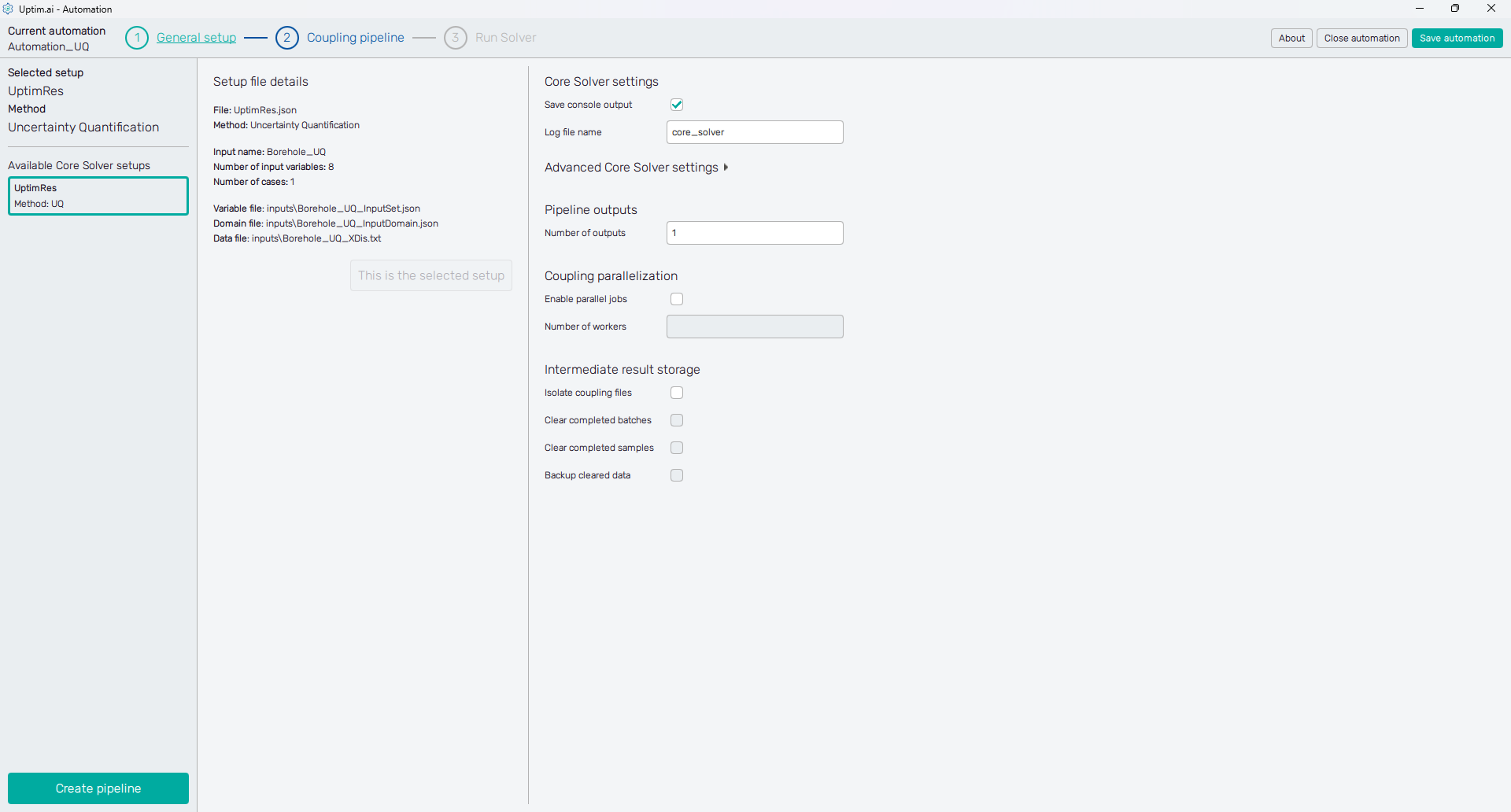
The Core Solver settings is a simple task in this case. We recommend turning on the console output saving that stores the log of the Core Solver. There is no need to enter and set the Advanced Core Solver settings.
Since the Python script we are about to include in the pipeline has only one output, the Number of Outputs in the Pipeline outputs section can remain at its default state (). Also, let's keep the Enable parallel jobs switch in the Coupling parallelization turned off. This will simplify the organization of files and folders related to computed data samples. Without the parallelization, we can also keep off the Isolate coupling files in the Intermediate result storage. Thus, no separate folders will be created for each sample.
The Coupling pipeline button is active as well as the Coupling pipeline item of the fishbone navigation bar at the top of the screen. Both of them lead to the next step.
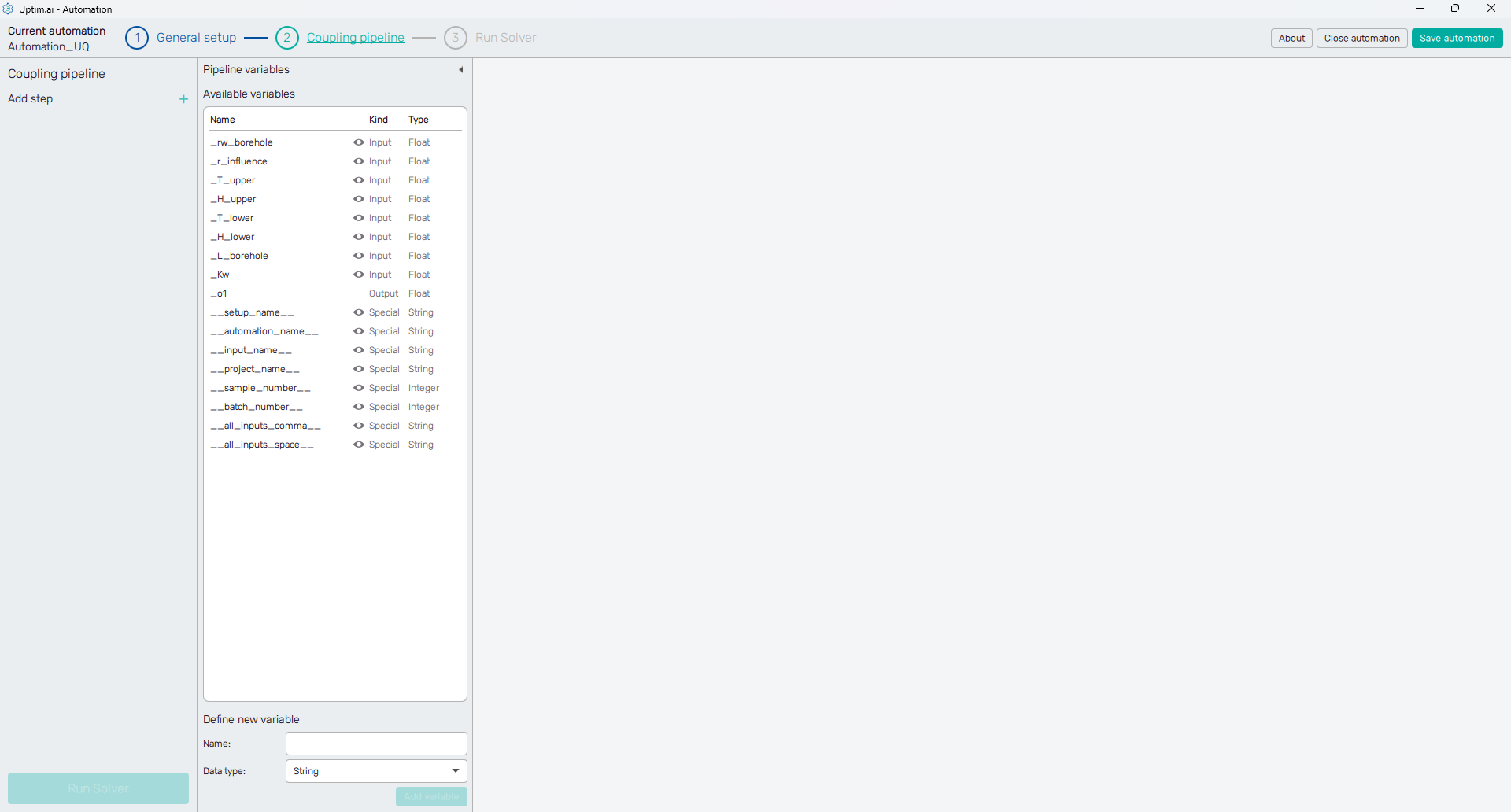
4.4: Add Executable step to the pipeline
Figure 15 shows the initial state of the Coupling pipeline setup. On the first sight you can see the collapsible Pipeline variables panel holding the auto-generated list of Available variables, some of these will be used later in the process.
To the left, there is the Coupling pipeline itself. Click the + icon next to the Add step label and select the Executable item from the drop-down menu. This will add the Executable step to the pipeline.
4.5: Set the Python script connection
Under the Command options section, you need to change the Type to Python. Right after,
define the Executable path of our Borehole.py file which is expected to be in the Project folder.
The Project folder option should be also selected as the Working directory.
The crucial setting here is about passing values of input variables to the Python script, which expects
these arguments. The task here is to copy the names of all input variables enclosed in double curly brackets
to the Arguments/options entry in the correct order. Right-clicking on an item from the list of
Available variables shows the menu allowing the user to copy either the name of the variable or the formatted
name (with brackets). Use the advantage of the automatically created special variable __all_inputs_space__
that will load all inputs as space-separated values.
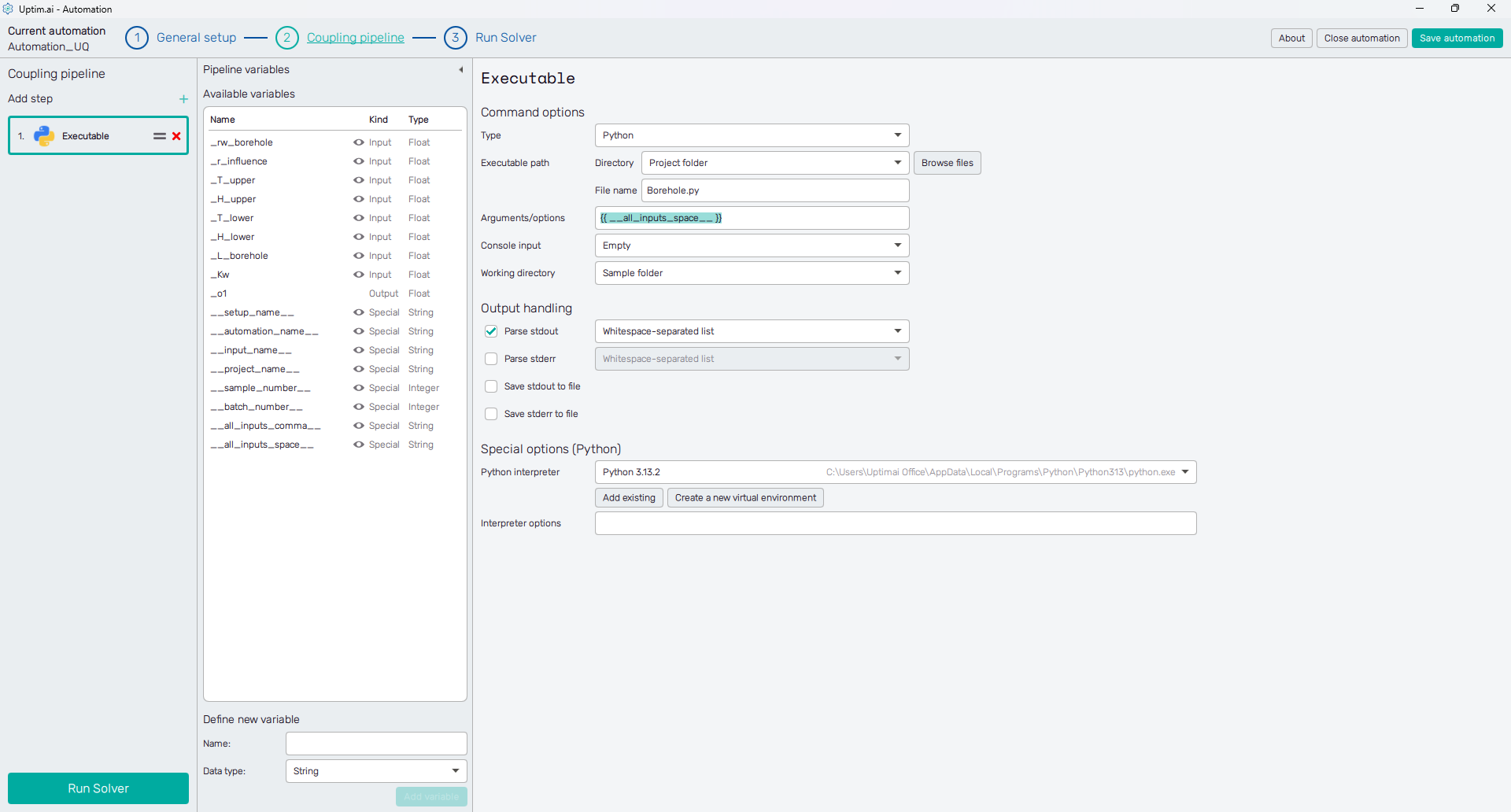
The last thing to set is selecting the Python interpreter in the Special options (Python) section. Be aware the script is using the numpy library, thus, this one should be available for the Python you are selecting.
Now, the Run Solver button is active as well as the Run Solver item of the fishbone navigation bar at the top of the screen. Both of them lead to the next step.
4.6: Run the Solver
Here comes the moment to click the Run button at the top of the screen and wait until the solver finishes all tasks. The solver will automatically run the coupling pipeline for all needed samples and will build the model. An Everything Finalized message will appear at the end of the log when the solver is finished.
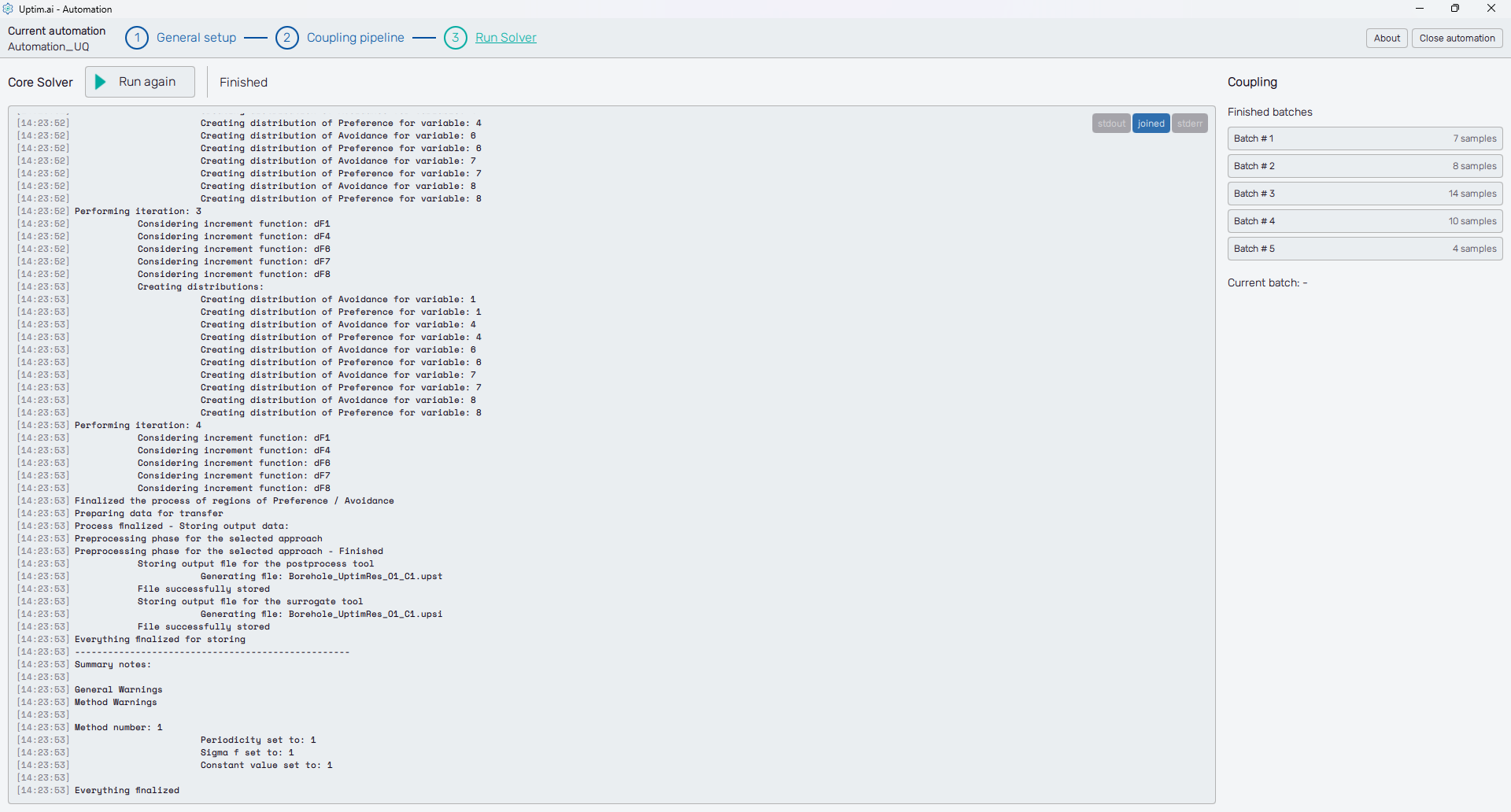
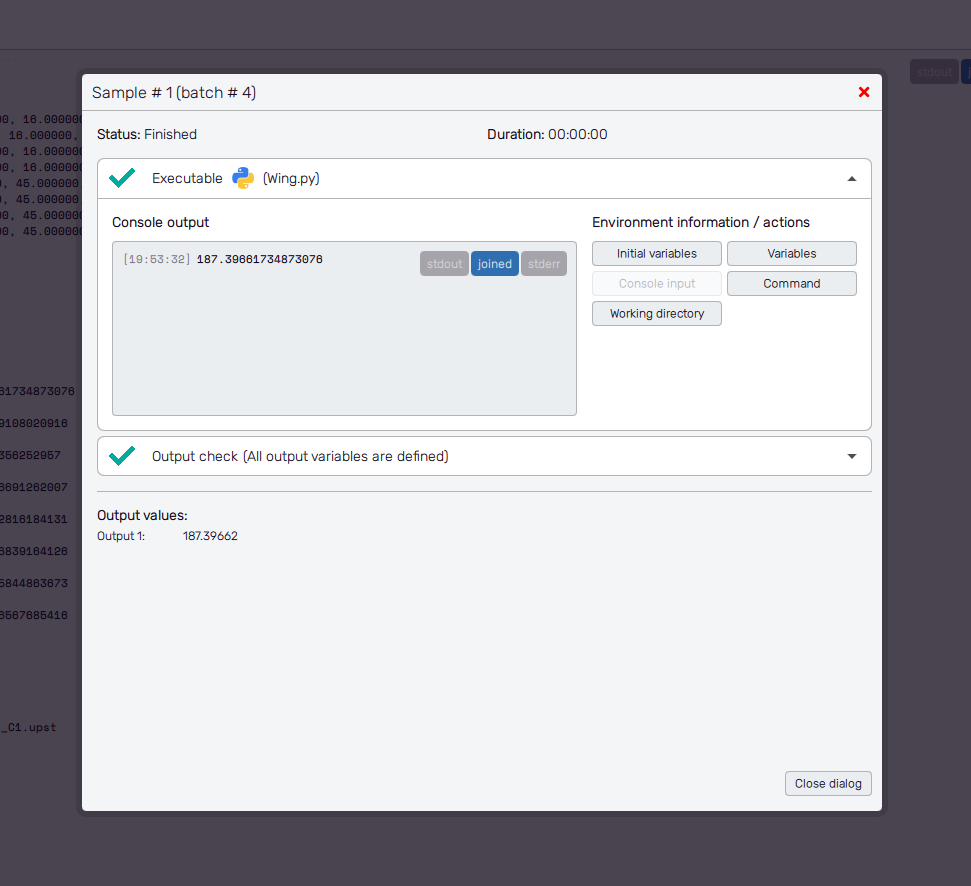
You can also check the obtained results directly. The Coupling section on the right holds the status of all pipelines, that are called in batches. Click an item from the list of Finished batches and hit the Inspect button of a sample you are interested in. Then, you can review every step of the corresponding coupling pipeline.
Part 5: Result Postprocess
5.1: Open the Postprocessor
Congratulations, you just ran your first Uptimai project! Now is the time to see the results. To do that we will open the Postprocessor from the Uptimai main interface.
5.2: Iterative file check
First of all, we will start opening the
Iterative file.
To do that we will click on the Borehole.itr file in the project files section.
The iterative files store all the samples that have been computed, so they can be reused in
future projects.
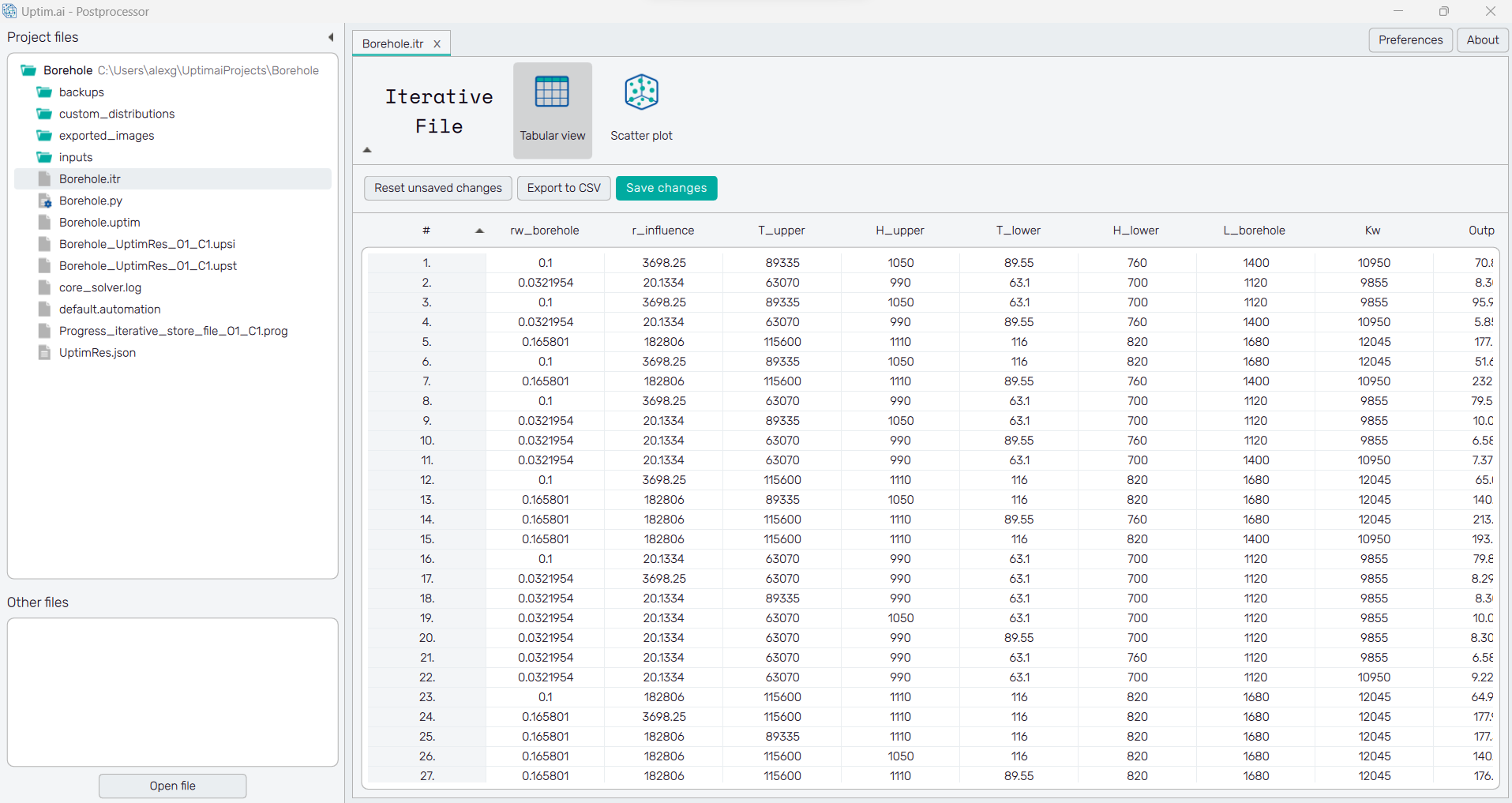
It has two ways of visualizing the data, or within a table which can be exported or as a scatter plot that allows to start visualizing the trends of how the outputs are distributed for each input.
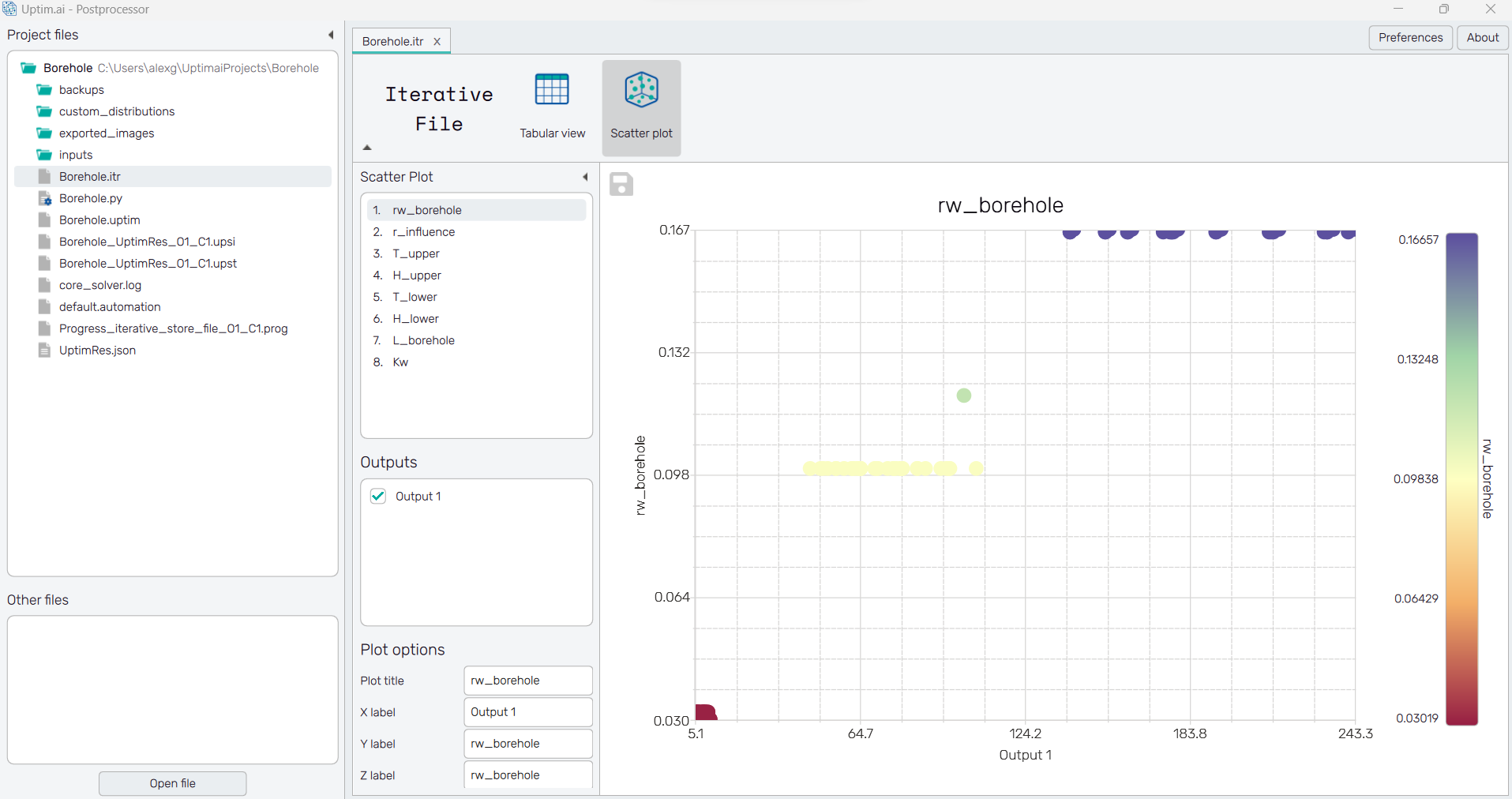
5.3: Open the model
Now we will open the model itself, opening the Borehole_UptimRes_O1_C1.upst.
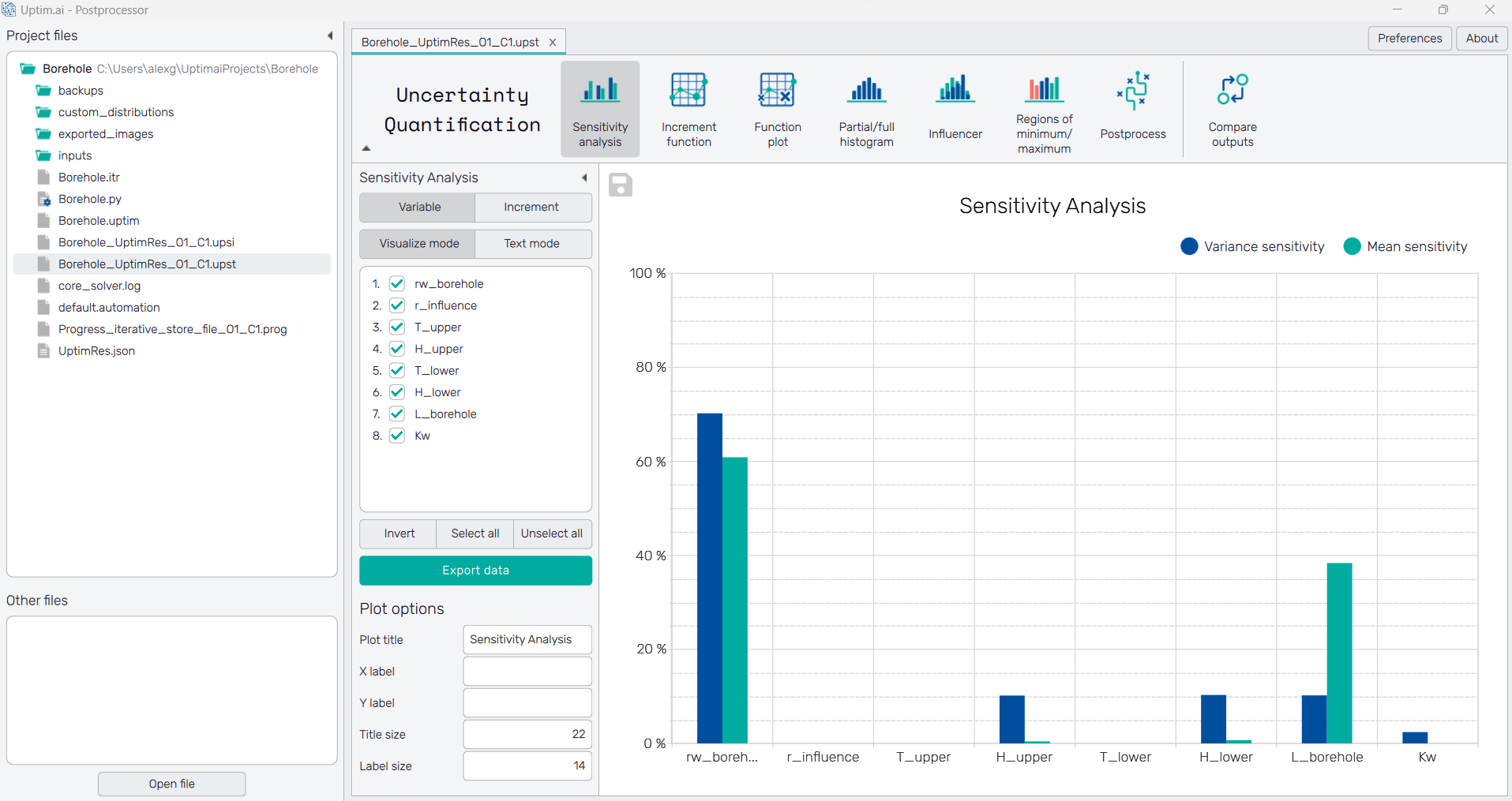
5.4: Sensitivity analysis
In the top section, we have all the features available, we will start with the Sensitivity analysis, which shows which variables are more important. In this case, we can easily see that variables r_influence, T_upper and T_lower are irrelevant and can be neglected from the study. Also, if we switch the sensitivity analysis to increment we can see not only the importance of variables, but if they are important by themselves or by interacting with other variables. In this case, the interactions don’t have a huge impact on the results.
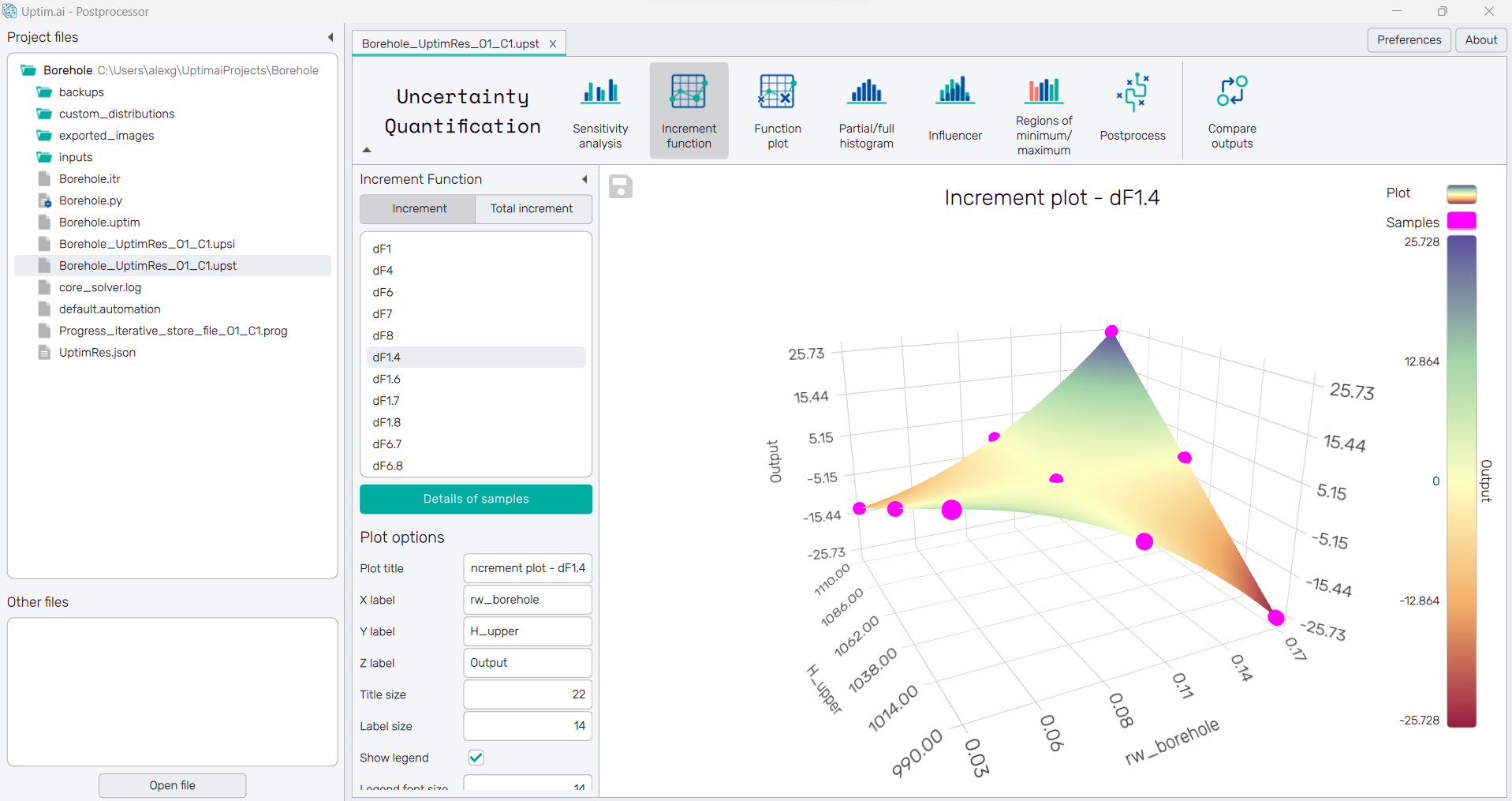
5.5: Increment function
In the Increment Function, we can see the independent effect of each increment, to understand how they are affecting the output and in which zones we want to be to optimize the solution.
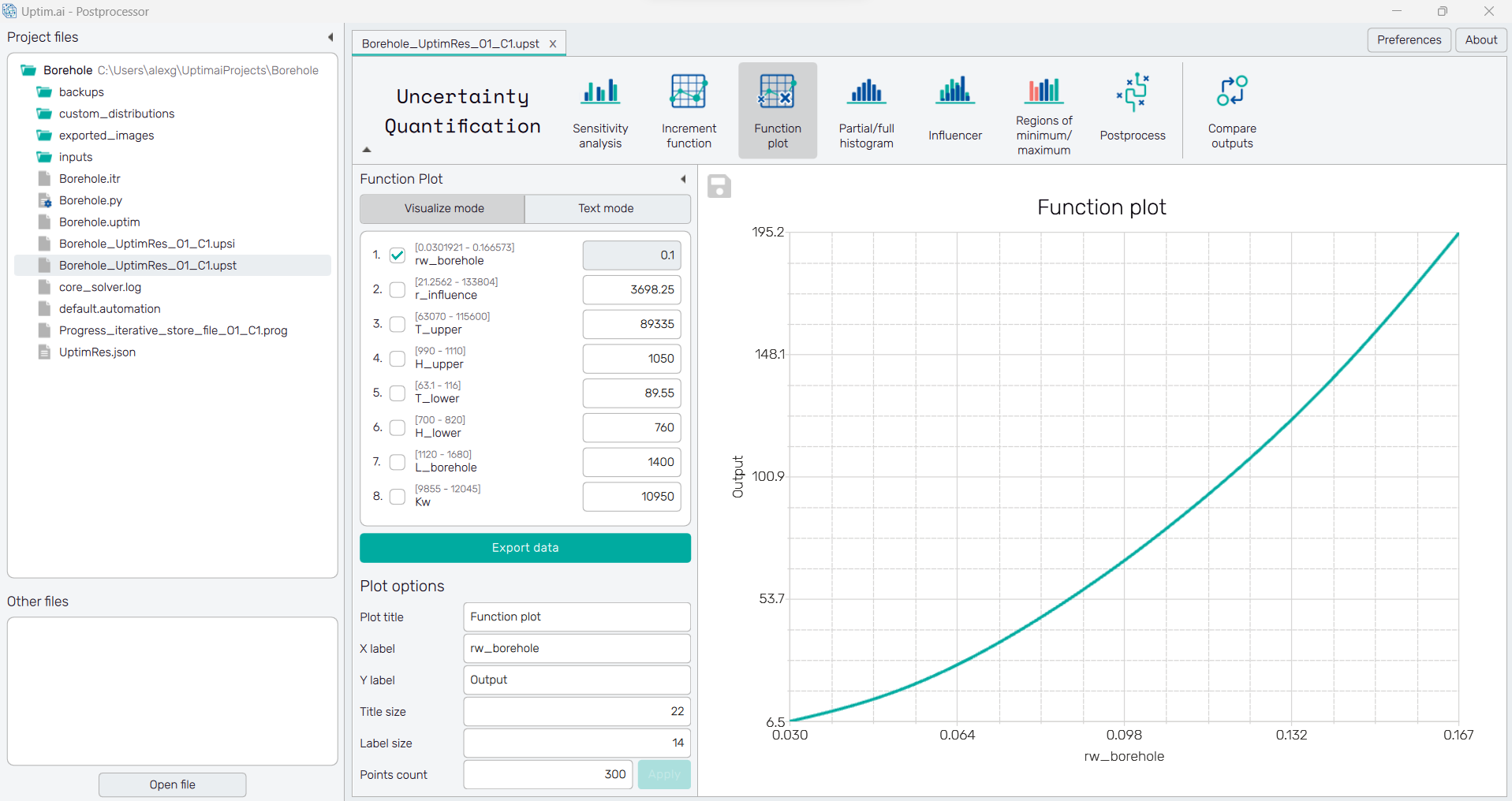
5.6: Function plot
In the Function plot, it is depicted the AI surrogate model so the user can extract the exact expected output for any possible combination of inputs. We can use both the Visualization mode and the Text mode.
5.7: Histogram plot
With the Partial/Full histogram, we can see the probability distribution of the output, to be able to see what are the expected zone of results given all the uncertainty from the inputs. Also, these can be shown for any combination of input variables or increment functions present in the model.
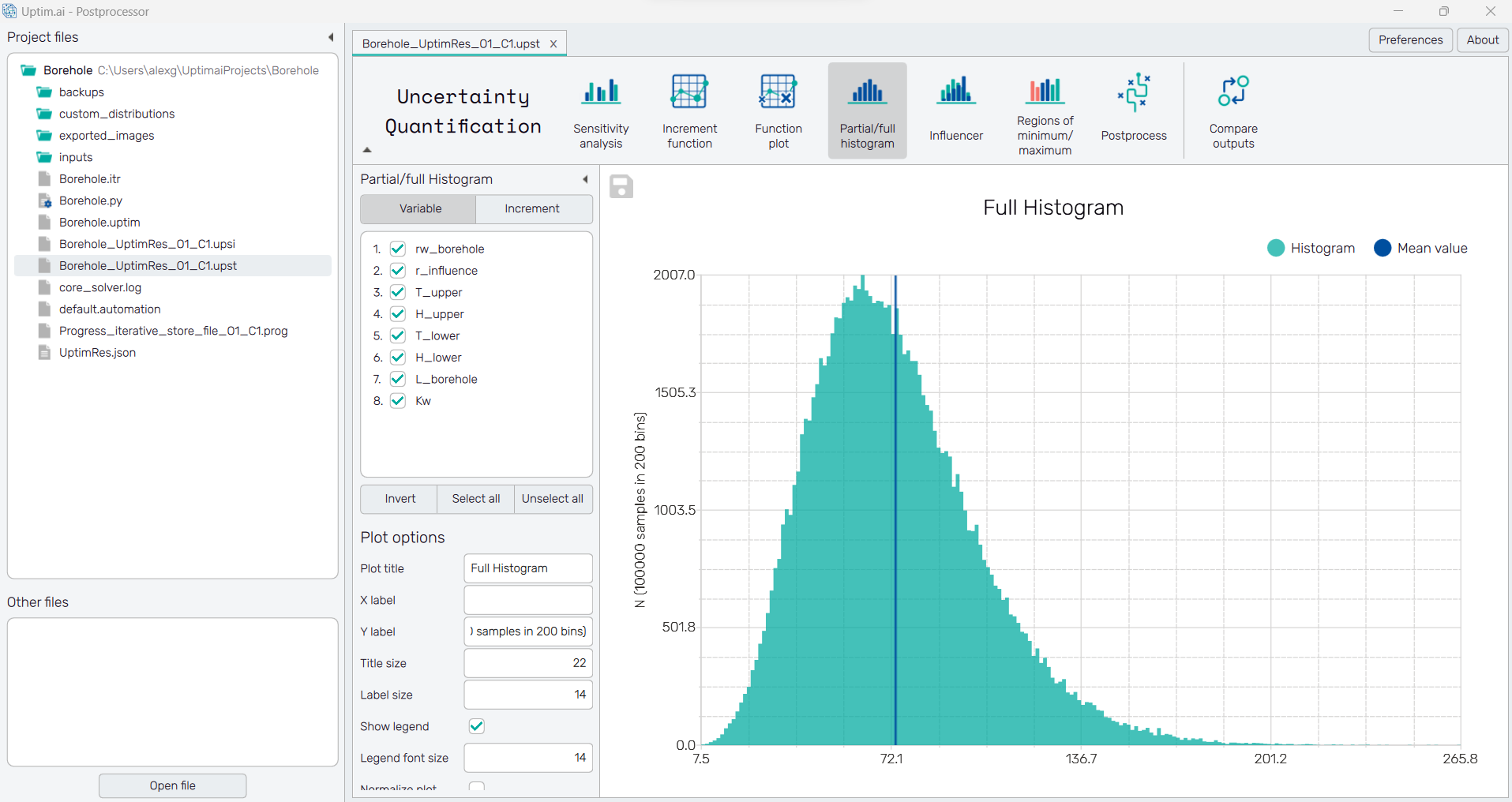
5.8: Influencer
With the Influencer, we can go a step further and discover how every variable or increment is actually affecting the output distribution, to understand how we can tune our problem to reduce the variability of the results in a desired way.
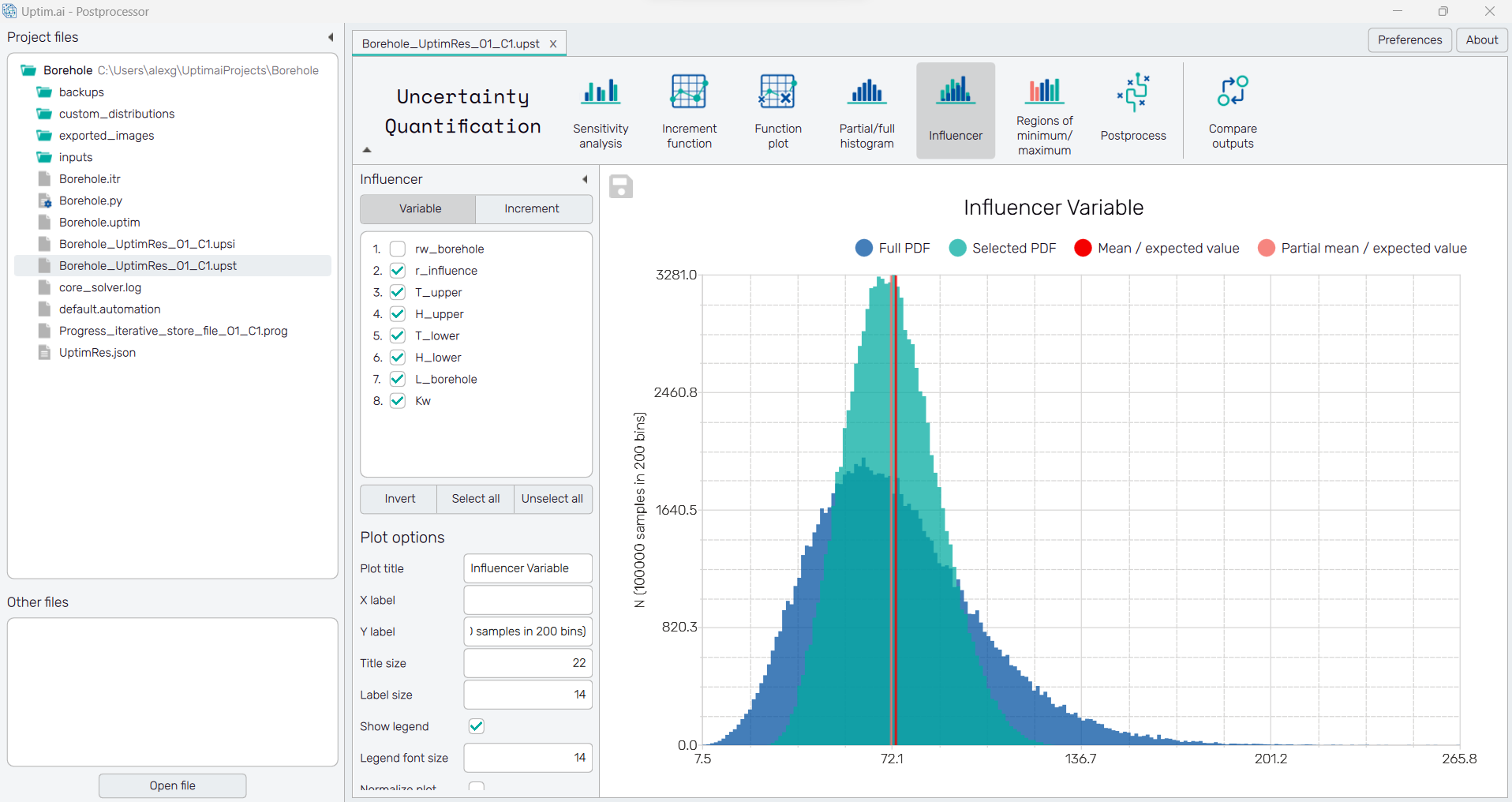
5.9: Regions of minimum/maximum
Finally, with the Regions of minimum/maximum, the software is doing a statistical optimization analysis. The Input option shows in which zones you should be from your original input distribution, no matter the uncertainties of the other variables have a statistical improvement on the output (to go to the maximum or the minimum).
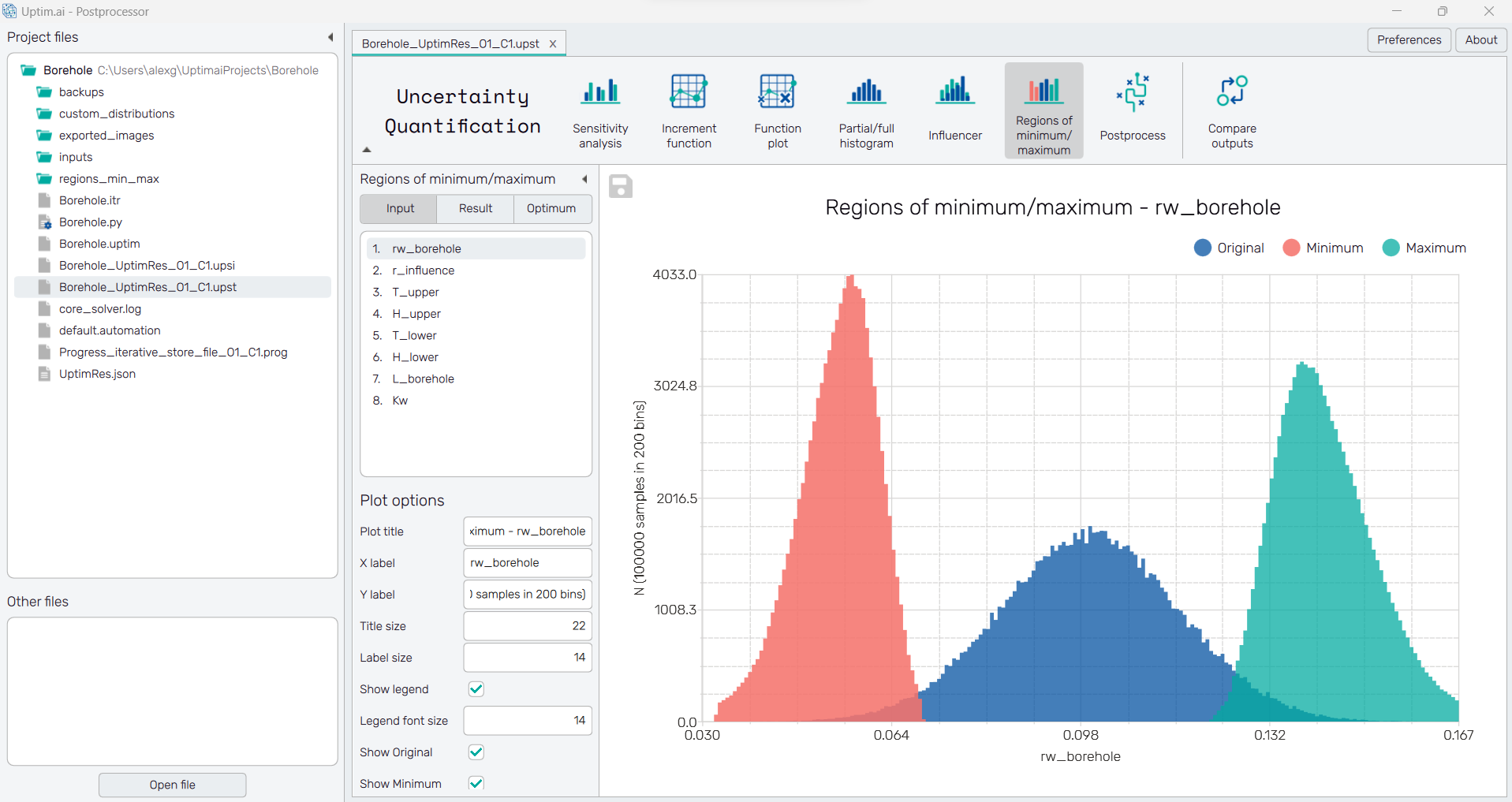
The Result option allows us to see which would be the expected result if the presented new input distributions were considered.
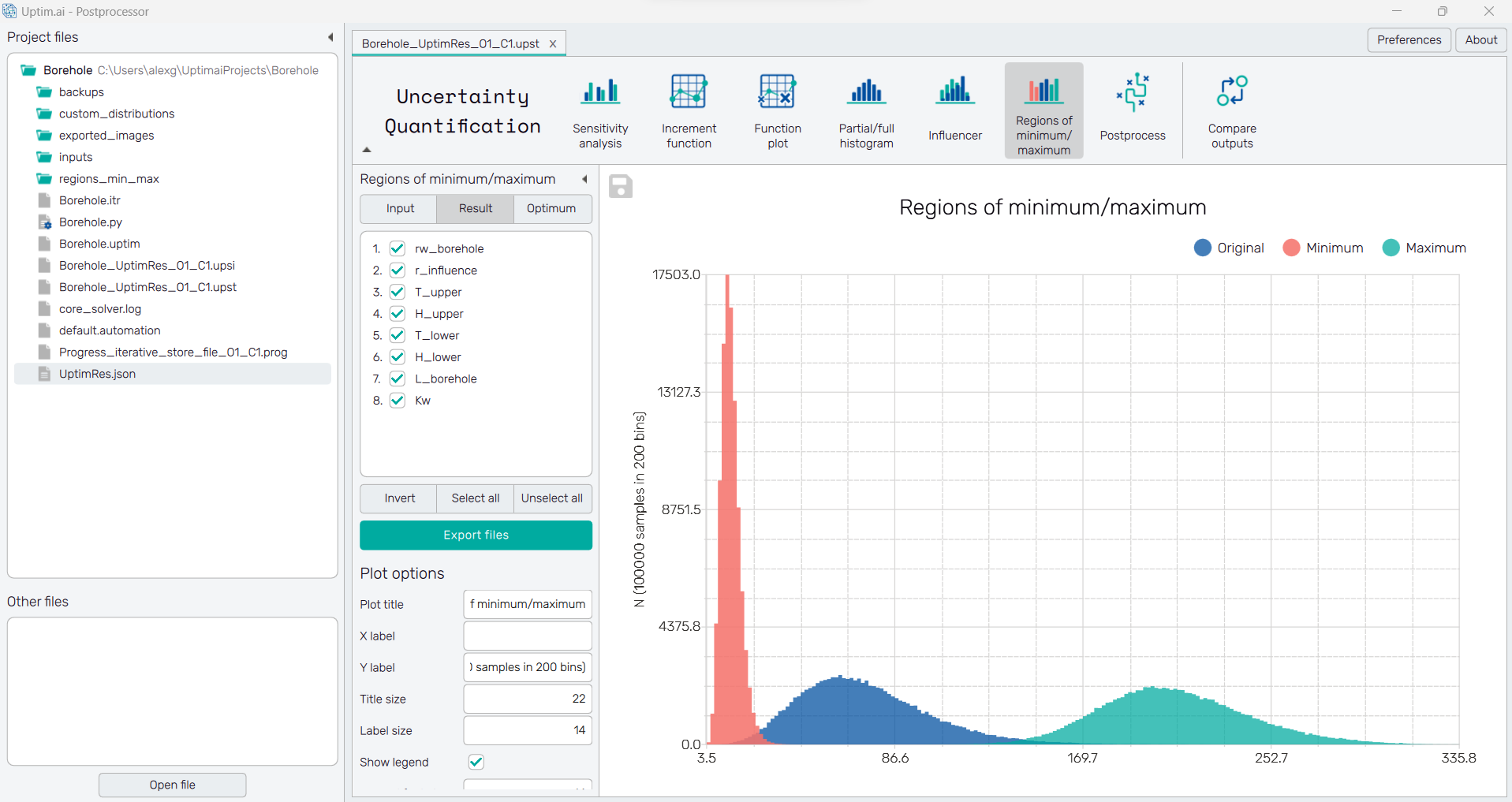
Finally, in the Optimum option, the software is showing what is the absolute maximum and the absolute minimum found with a Monte Carlo approach, and where it is located.
Part 6: AI Surrogate Model
6.1: Open the AI Surrogate Model
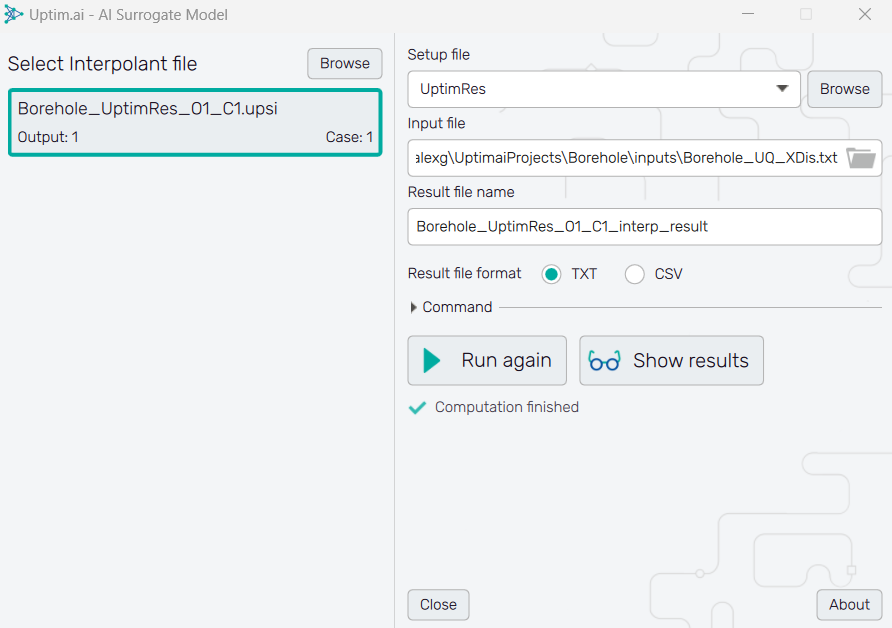
The last feature of this tutorial is the AI surrogate model, which allows for easy access to the model and to receive the output for any set of samples given. We can access, as all the other features, from the Uptimai main interface.
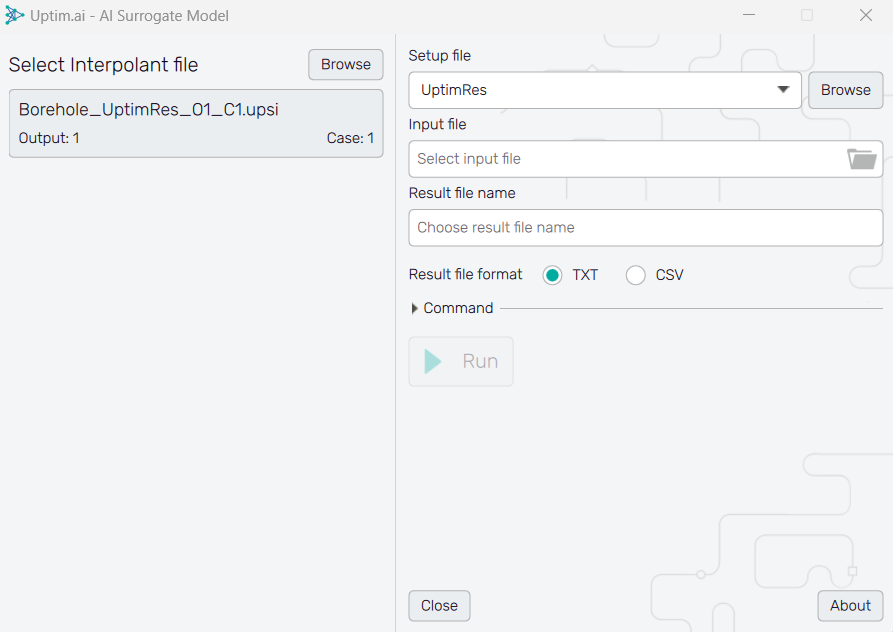
6.2: Select the model
First, we will need to Select Interpolant file (the model), that we have previously created
in the solver. The Borehole_UptimRes_O1_C1.upsi file is a 'lite' version of the result file
without data required for visualizations in the
Postprocessor.
6.3: Define other files
Then we will need to select an Input File, which has to be in a comma-separated format with
as many rows as samples wanted and as many columns as inputs have the problem.
For this example, we can use the Borehole_UQ_XDis.txt file situated, in the inputs folder
inside your project. Do not forget to select the correct Setup file that was used for the
learning of the model. In our case, it is the UptimRes.json.
6.4: Evaluate the surrogate model
Finally, we can change the Result file name if needed, and press the Run button. A file will be generated in the project folder with the output given from the model from all the samples that were fed.